AIDL 使用步骤
1.创建 UserManager.aidl 接口文件,声明作为 Server 端的远程 Service 具有哪些能力
UserManager.aidl:
package com.me.guanpj.binder;
import com.me.guanpj.binder.User;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
interface UserManager {
void addUser(in User user);
List getUserList();
}对于对象引用,还需要引入实体类
User.aidl:
// User.aidl
package com.me.guanpj.binder;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
parcelable User;跨进程传输对象必须实现 Parcelable 接口
User.java
public class User implements Parcelable {
public int id;
public String name;
public User() {}
public User(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
protected User(Parcel in) {
id = in.readInt();
name = in.readString();
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) {
dest.writeInt(id);
dest.writeString(name);
}
@Override
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
public static final Creator CREATOR = new Creator() {
@Override
public User createFromParcel(Parcel in) {
return new User(in);
}
@Override
public User[] newArray(int size) {
return new User[size];
}
};
}生成的 UserManager 类如下:
UserManager.java:
package com.me.guanpj.binder;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
public interface UserManager extends android.os.IInterface
{
/** Local-side IPC implementation stub class. */
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements com.me.guanpj.binder.UserManager
{
private static final java.lang.String DESCRIPTOR = "com.me.guanpj.binder.UserManager";
/** Construct the stub at attach it to the interface. */
public Stub()
{
this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR);
}
/**
* Cast an IBinder object into an com.me.guanpj.binder.UserManager interface,
* generating a proxy if needed.
*/
public static com.me.guanpj.binder.UserManager asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj)
{
if ((obj==null)) {
return null;
}
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin!=null)&&(iin instanceof com.me.guanpj.binder.UserManager))) {
return ((com.me.guanpj.binder.UserManager)iin);
}
return new com.me.guanpj.binder.UserManager.Stub.Proxy(obj);
}
@Override public android.os.IBinder asBinder()
{
return this;
}
@Override public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException
{
java.lang.String descriptor = DESCRIPTOR;
switch (code)
{
case INTERFACE_TRANSACTION:
{
reply.writeString(descriptor);
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_addUser:
{
data.enforceInterface(descriptor);
com.me.guanpj.binder.User _arg0;
if ((0!=data.readInt())) {
_arg0 = com.me.guanpj.binder.User.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);
}
else {
_arg0 = null;
}
this.addUser(_arg0);
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_getUserList:
{
data.enforceInterface(descriptor);
java.util.List _result = this.getUserList();
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeTypedList(_result);
return true;
}
default:
{
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
}
}
}
private static class Proxy implements com.me.guanpj.binder.UserManager
{
private android.os.IBinder mRemote;
Proxy(android.os.IBinder remote)
{
mRemote = remote;
}
@Override public android.os.IBinder asBinder()
{
return mRemote;
}
public java.lang.String getInterfaceDescriptor()
{
return DESCRIPTOR;
}
@Override public void addUser(com.me.guanpj.binder.User user) throws android.os.RemoteException
{
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
if ((user!=null)) {
_data.writeInt(1);
user.writeToParcel(_data, 0);
}
else {
_data.writeInt(0);
}
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_addUser, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
}
finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
}
@Override public java.util.List getUserList() throws android.os.RemoteException
{
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
java.util.List _result;
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_getUserList, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
_result = _reply.createTypedArrayList(com.me.guanpj.binder.User.CREATOR);
}
finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
return _result;
}
}
static final int TRANSACTION_addUser = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 0);
static final int TRANSACTION_getUserList = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 1);
}
public void addUser(com.me.guanpj.binder.User user) throws android.os.RemoteException;
public java.util.List getUserList() throws android.os.RemoteException;
}3.创建 Service,实现 UserManager.Stub 类并将该实现类的实例在 onBind 方法返回
MyService.java:
public class MyService extends Service {
class UserManagerNative extends UserManager.Stub {
List users = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
public void addUser(User user) {
Log.e("gpj", "进程:" + Utils.getProcessName(getApplicationContext())
+ ",线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "————" + "Server 执行 addUser");
users.add(user);
}
@Override
public List getUserList() {
Log.e("gpj", "进程:" + Utils.getProcessName(getApplicationContext())
+ ",线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "————" + "Server 执行 getUserList");
return users;
}
}
private UserManagerNative mUserManagerNative = new UserManagerNative();
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
Log.e("gpj", "进程:" + Utils.getProcessName(getApplicationContext())
+ ",线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "————" + "Server onBind");
return mUserManagerNative;
}
}4.在作为 Client 端的 Activity 中,绑定远程 Service 并得到 Server 的代理对象
5.通过 Server 代理对象,调用 Server 的具体方法
MainActivity.java:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
Button btnBind;
Button btnAddUser;
Button btnGetSize;
TextView tvResult;
IUserManager mUserManager;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
btnBind = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_bind);
btnAddUser = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_add_user);
btnGetSize = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_get_size);
btnBind.setOnClickListener(this);
btnAddUser.setOnClickListener(this);
btnGetSize.setOnClickListener(this);
tvResult = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.txt_result);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
unbindService(mConn);
super.onDestroy();
}
private ServiceConnection mConn = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
Log.e("gpj", "进程:" + Utils.getProcessName(getApplicationContext())
+ ",线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "————" + "Client onServiceConnected");
mUserManager = UserManagerImpl.asInterface(service);
try {
//注册远程服务死亡通知
service.linkToDeath(mDeathRecipient, 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
mUserManager = null;
}
};
private IBinder.DeathRecipient mDeathRecipient = new IBinder.DeathRecipient() {
@Override
public void binderDied() {
if (mUserManager != null) {
mUserManager.asBinder().unlinkToDeath(mDeathRecipient, 0);
mUserManager = null;
//重新绑定服务
bindService();
}
}
};
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.btn_bind:
bindService();
break;
case R.id.btn_add_user:
if (null != mUserManager) {
try {
Log.e("gpj", "线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "————" +"Client 调用 addUser");
mUserManager.addUser(new User(111, "gpj"));
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "先绑定 Service 才能调用方法", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
break;
case R.id.btn_get_size:
if (null != mUserManager) {
try {
Log.e("gpj", "线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "————" +"Client 调用 getUserList");
List userList = mUserManager.getUserList();
tvResult.setText("getUserList size:" + userList.size());
Log.e("gpj", "线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "————" +"调用结果:" + userList.size());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "先绑定 Service 才能调用方法", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
break;
default:
}
}
private void bindService() {
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction("com.me.guanpj.binder");
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName("com.me.guanpj.binder", "com.me.guanpj.binder.MyService"));
Log.e("gpj", "进程:" + Utils.getProcessName(getApplicationContext())
+ ",线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "————" + "开始绑定服务");
bindService(intent, mConn, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
}AIDL 的实现过程
为了便于理解,这里用一个 Demo 来展示 AIDL 的实现过程:Activity 作为 Client 与作为 Server 端的远程 Service 实现数据交互,在绑定远程 Service 之后,点击 AddUser 后 Service 会将 Client 端传进来的 User 对象加入列表中,点击 GetSize 后远程 Service 将会把列表的长度返回给客户端。建议在继续阅读之前先查看或者运行一下项目源码:
在项目中创建 UserManager.aidl 文件之后,系统会自动在 build 目录生成一个与 UserManager.java 接口类,它继承了 IInterface 接口,UserManager 接口只有一个静态抽象类 Stub,Stub 继承自 Binder 并实现了 UserManager 接口,Stub 里面也有一个静态内部类 Proxy,Proxy 也继承了 UserManager(是不是有点乱,乱就对了,我也很乱)。
如此嵌套是为了避免有多个 .aidl 文件的时候自动生成这些类的类名不会重复,为了提高代码可读性,我们将生成的 UserManager 和 Stub 类 拆解并重新命名成了 IUserManager 类和 UserManagerImpl 类并在关键方法上添加了注释或者 Log。
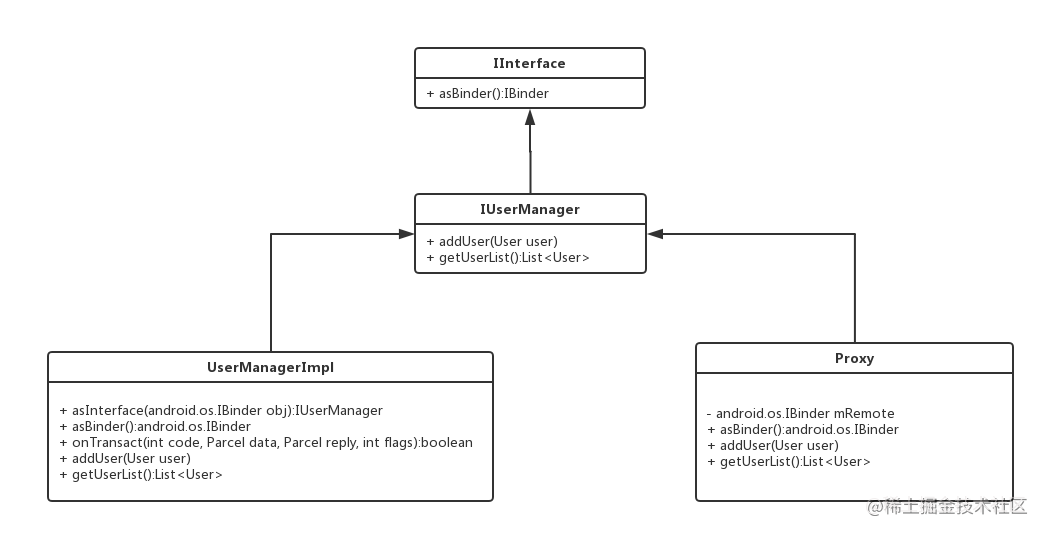
IUserManager.java:
public interface IUserManager extends android.os.IInterface {
//唯一性标识
static final java.lang.String DESCRIPTOR = "com.me.guanpj.binder.IUserManager";
//方法标识,用十六进制表示
int TRANSACTION_addUser = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 0);
int TRANSACTION_getUserList = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 1);
//Server 具有的能力
void addUser(User user) throws android.os.RemoteException;
List getUserList() throws android.os.RemoteException;
}UserManagerImpl.java:
public abstract class UserManagerImpl extends Binder implements IUserManager {
/**
* Construct the mLocalStub at attach it to the interface.
*/
public UserManagerImpl() {
this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR);
}
/**
* 根据 Binder 本地对象或者代理对象返回 IUserManager 接口
*/
public static IUserManager asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj) {
if ((obj == null)) {
return null;
}
//查找本地对象
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin != null) && (iin instanceof IUserManager))) {
Log.e("gpj", "线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "————" + "返回本地对象");
return ((IUserManager) iin);
}
Log.e("gpj", "线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "————" + "返回代理对象");
return new UserManagerImpl.Proxy(obj);
}
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder() {
return this;
}
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case INTERFACE_TRANSACTION: {
reply.writeString(DESCRIPTOR);
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_addUser: {
Log.e("gpj", "线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "————" + "本地对象通过 Binder 执行 addUser");
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
User arg0;
if ((0 != data.readInt())) {
//取出客户端传递过来的数据
arg0 = User.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);
} else {
arg0 = null;
}
//调用 Binder 本地对象
this.addUser(arg0);
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_getUserList: {
Log.e("gpj", "线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "————" + "本地对象通过 Binder 执行 getUserList");
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
//调用 Binder 本地对象
List result = this.getUserList();
reply.writeNoException();
//将结果返回给客户端
reply.writeTypedList(result);
return true;
}
default:
break;
}
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
}
private static class Proxy implements IUserManager {
private android.os.IBinder mRemote;
Proxy(android.os.IBinder remote) {
mRemote = remote;
}
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder() {
return mRemote;
}
public java.lang.String getInterfaceDescriptor() {
return DESCRIPTOR;
}
@Override
public void addUser(User user) throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
if (user != null) {
_data.writeInt(1);
user.writeToParcel(_data, 0);
} else {
_data.writeInt(0);
}
Log.e("gpj", "线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "————" + "代理对象通过 Binder 调用 addUser");
mRemote.transact(UserManagerImpl.TRANSACTION_addUser, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
}
@Override
public List getUserList() throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
List _result;
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
Log.e("gpj", "线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "————" + "代理对象通过 Binder 调用 getUserList");
mRemote.transact(UserManagerImpl.TRANSACTION_getUserList, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
_result = _reply.createTypedArrayList(User.CREATOR);
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
return _result;
}
}
}再进行分析之前,先了解几个概念:
- IInterface : 从注释中的说明看出,声明(自动生成或者手动创建)AIDL 性质的接口必须继承这个接口,这个接口只有一个 IBinder asBinder() 方法,实现它的类代表它能够进程跨进程传输( Binder 本地对象)或者持有能够进程跨进程传输的对象的引用(Binder 代理对象)。
- IUserManager : 它同样是一个接口,它继承了 IInterface 类,并声明了 Server 承诺给 Client 的能力
- IBinder : 它也是一个接口,实现这个接口的对象就具有了跨进程传输的能力,在跨进程数据流经驱动的时候,驱动会识别IBinder类型的数据,从而自动完成不同进程Binder本地对象以及Binder代理对象的转换。
- Binder : 代表 Binder 本地对象,BinderProxy 类是它的内部类,是 Server 端 Binder 对象的本地代理,它们都继承了 IBinder 接口,因此都能跨进程进行传输,Binder 驱动在跨进程传输的时候会将这两个对象自动进行转换。
- UserManagerImpl : 它继承了 Binder 并实现了 IInterface 接口,说明它是 Server 端的 Binder 本地对象,并拥有 Server 承诺给 Client 的能力。
先从 MainActivity 中绑定服务后的回调方法着手:
private ServiceConnection mConn = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
mUserManager = UserManagerImpl.asInterface(service);
try {
//注册远程服务死亡通知
service.linkToDeath(mDeathRecipient, 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
mUserManager = null;
}
};onServiceConnected 的参数中,第一个是 Service 组件的名字,表示哪个服务被启动了,重点是类型为 IBinder 的第二个参数,在 Service.java 中的 onBind 方法中,已经把 Server 端的本地对象 UserManagerNative 实例返回给 Binder 驱动了:
private UserManagerNative mUserManagerNative = new UserManagerNative();
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mUserManagerNative;
}因此,当该服务被绑定的时候,Binder 驱动会为根据该服务所在的进程决定 是返回本地对象还是代理对象给客户端,当 Service 与 MainActivity 位于同一个进程当中的时候,onServiceConnected 返回 Binder 本地对象——即 UserManagerNative 对象给客户端;当 Service 运行在不同进程中的时候,返回的是 BinderProxy 对象。
接着,在将这个 IBinder 对象传给 UserManagerImpl 的 asInterface 方法并返回 IUserManager 接口,asInterface 方法实现如下:
/**
* 根据 Binder 本地对象或者代理对象返回 IUserManager 接口
*/
public static IUserManager asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj) {
if ((obj == null)) {
return null;
}
//查找本地对象
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin != null) && (iin instanceof IUserManager))) {
return ((IUserManager) iin);
}
return new UserManagerImpl.Proxy(obj);
}首先,会根据 DESCRIPTOR 调用 IBinder 对象的 queryLocalInterface 方法,那么就得看 IBinder 的实现类怎么处理这个方法了:
在 Binder 类中的实现:
public @Nullable IInterface queryLocalInterface(@NonNull String descriptor) {
//判断 mDescriptor 跟参数 DESCRIPTOR 相同,返回 mOwner
if (mDescriptor != null && mDescriptor.equals(descriptor)) {
return mOwner;
}
return null;
}那么这个 mOwner 和 mDescriptor 又是什么时候被赋值的呢?答案在 Binder 的子类 UserManagerImpl 的构造方法里面,:
public UserManagerImpl() {
//将 UserManagerImpl 和 DESCRIPTOR 注入到父类(Binder)
this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR);
}在 Binder$BinderProxy 类中的实现:
BinderProxy 并不是 Binder 本地对象,而是 Binder 的本地代理,因此 queryLocalInterface 返回的是 null:
public IInterface queryLocalInterface(String descriptor) {
return null;
}综上两点可以看出,如果 obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR) 方法存在返回值并且是 IUserManager 类型的对象,那么它就是 Binder 本地对象,将它直接返回给 Client 调用;否则,使用 UserManagerImpl$Proxy 类将其进行包装后再返回,Proxy 类也实现了 IUserManager 接口,因此,在 Client 眼中,它也具有 Server 承诺给 Client 的能力,那么,经过包装后的对象怎么和 Server 进行交互呢?
首先,它会把 BinderProxy 对象保存下来:
Proxy(android.os.IBinder remote) {
mRemote = remote;
}然后,实现 IUserManager 的方法:
@Override
public void addUser(User user) throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
if (user != null) {
_data.writeInt(1);
//将 user 对象的值写入 _data
user.writeToParcel(_data, 0);
} else {
_data.writeInt(0);
}
//通过 transact 跟 Server 交互
mRemote.transact(UserManagerImpl.TRANSACTION_addUser, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
}
@Override
public List getUserList() throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
List _result;
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
//通过 transact 跟 Server 交互
mRemote.transact(UserManagerImpl.TRANSACTION_getUserList, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
//获取 Server 的返回值并进程转换
_result = _reply.createTypedArrayList(User.CREATOR);
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
return _result;
}可以看到,不管什么方法,都是是将服务端的方法代号、处理过的参数和接收返回值的对象等通过 mRemote.transact 方法 Server 进行交互,mRemote 是 BinderProxy 类型,在 BinderProxy 类中,最终调用的是 transactNative 方法:
public native boolean transactNative(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags) throws RemoteException;它的最终实现在 Native 层进行,Binder 驱动会通过 ioctl 系统调用唤醒 Server 进程,并调用 Server 本地对象的 onTransact 函数:
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case INTERFACE_TRANSACTION: {
reply.writeString(DESCRIPTOR);
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_addUser: {
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
User arg0;
if ((0 != data.readInt())) {
//取出客户端传递过来的数据
arg0 = User.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);
} else {
arg0 = null;
}
//调用 Binder 本地对象
this.addUser(arg0);
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_getUserList: {
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
//调用 Binder 本地对象
List result = this.getUserList();
reply.writeNoException();
//将结果返回给客户端
reply.writeTypedList(result);
return true;
}
default:
break;
}
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
}在 Server 进程中,onTransact 会根据 Client 传过来的方法代号决定调用哪个方法,得到结果后又会通过 Binder 驱动返回给 Client。
总结
回溯到 onServiceConnected 回调方法,待服务连接成功后,Client 就需要跟 Server 进行交互了,如果 Server 跟 Client 在同一个进程中,Client 可以直接调用 Server 的本地对象 ,当它们不在同一个进程中的时候,Binder 驱动会自动将 Server 的本地对象转换成 BinderProxy 代理对象,经过一层包装之后,返回一个新的代理对象给 Client。这样,整个 IPC 的过程就完成了。
文章来源于互联网:Android Binder 机制——AIDL 的使用和原理分析
1、本站所有资源均从互联网上收集整理而来,仅供学习交流之用,因此不包含技术服务请大家谅解!
2、本站不提供任何实质性的付费和支付资源,所有需要积分下载的资源均为网站运营赞助费用或者线下劳务费用!
3、本站所有资源仅用于学习及研究使用,您必须在下载后的24小时内删除所下载资源,切勿用于商业用途,否则由此引发的法律纠纷及连带责任本站和发布者概不承担!
4、本站站内提供的所有可下载资源,本站保证未做任何负面改动(不包含修复bug和完善功能等正面优化或二次开发),但本站不保证资源的准确性、安全性和完整性,用户下载后自行斟酌,我们以交流学习为目的,并不是所有的源码都100%无错或无bug!如有链接无法下载、失效或广告,请联系客服处理!
5、本站资源除标明原创外均来自网络整理,版权归原作者或本站特约原创作者所有,如侵犯到您的合法权益,请立即告知本站,本站将及时予与删除并致以最深的歉意!
6、如果您也有好的资源或教程,您可以投稿发布,成功分享后有站币奖励和额外收入!
7、如果您喜欢该资源,请支持官方正版资源,以得到更好的正版服务!
8、请您认真阅读上述内容,注册本站用户或下载本站资源即您同意上述内容!
原文链接:https://www.dandroid.cn/archives/21136,转载请注明出处。


评论0