1. 如何新建一个系统 App 项目
使用 Android Studio 新建一个空项目 FirstSystemApp,包名设置为 com.yuandaima.firstsystemapp,语言选择 Java。后面为叙述方便称该项目为 as 项目。
接着在 jelly/rice14 目录下创建如下的目录和文件:
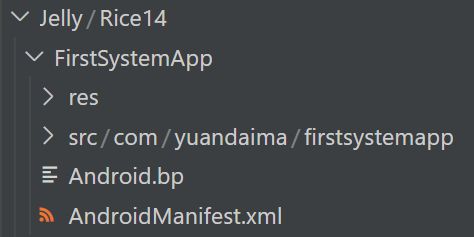
接着将 as 项目中的 res 文件下的资源文件拷贝到 Jelly/Rice14/FirstSystemApp/res 中,把 as 项目中的 MainActivity.java 拷贝到 Jelly/Rice14/FirstSystemApp/src/com/yuandaima/firstsystemapp 中。
接着修改已添加的 AndroidManifest.xml 文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.yuandaima.firstsystemapp">
<application
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.FirstSystemApp">
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
<meta-data
android:name="android.app.lib_name"
android:value="" />
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>接着修改已添加的 Android.bp 文件:
android_app {
name: "FirstSystemApp",
srcs: ["src/**/*.java"],
resource_dirs: ["res"],
manifest: "AndroidManifest.xml",
platform_apis: true,
sdk_version: "",
certificate: "platform",
product_specific: true,
//依赖
static_libs: ["androidx.appcompat_appcompat",
"com.google.android.material_material",
"androidx-constraintlayout_constraintlayout"],
}至此我们的系统 App 就创建好了。
接着在我们的 Product 中添加这个App,修改 device/Jelly/Rice14/Rice14.mk:
# 添加以下内容
PRODUCT_PACKAGES += FirstSystemApp接着编译系统,启动虚拟机,打开 app:
source build/envsetup.sh
lunch Rice14-eng
make -j16
emulator 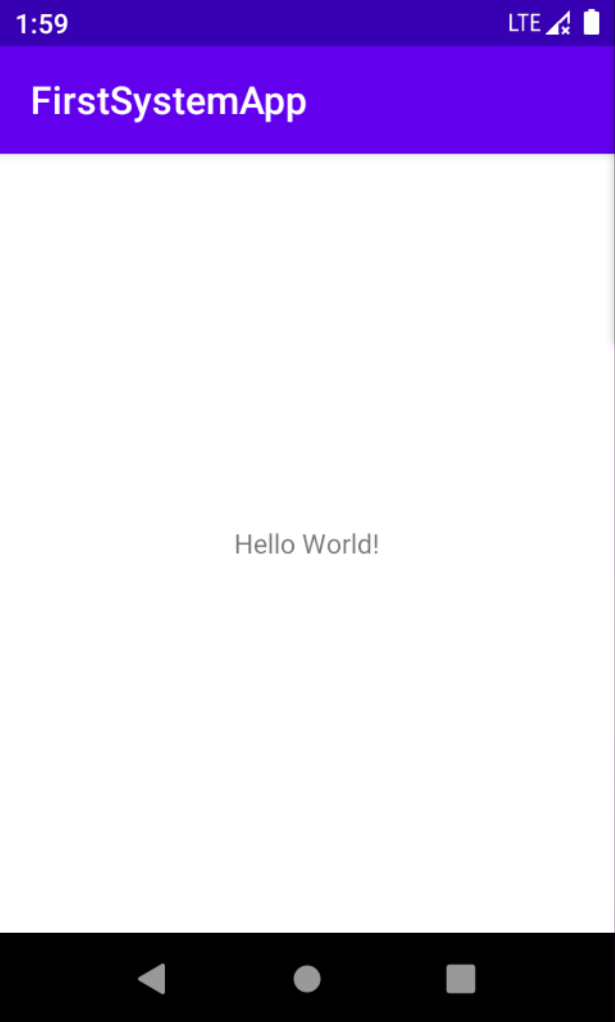
2. 系统 App 与 普通 App 的差异
2.1 系统 App 可以使用更多的 api
当我们在 Android.bp 中配置了:
platform_apis: true,
sdk_version: "",当 platform_apis 为 true 时,sdk_version 必须为空。这种情况下我们的 app 会使用平台 API 进行编译而不是 SDK,这样我们的 App 就能访问到非 SDK API 了。关于 SDK API 和非 SDK API 的内容可以参考官方文档
2.2 系统 App 的签名
AOSP 内置了 apk 签名文件,我们可以在 Android.bp 中通过 certificate 配置系统 app 的签名文件,certificate 的值主要有一下几个选项:
- testkey:普通 apk,默认情况下使用
- platform:该 apk 完成一些系统的核心功能。经过对系统中存在的文件夹的访问测试,这种方式编译出来的 APK 所在进程的 UID 为system
- shared:该 apk 需要和 home/contacts 进程共享数据
- media:该 apk 是 media/download 系统中的一环
- PRESIGNED:表示 这个 apk 已经签过名了,系统不需要再次签名;
2.3 系统 App 能使用更多的权限
当 Android.bp 中的 privileged 被配置为 true 时,我们的系统 App 在添加特许权限许可名单后,能使用 signatureOrSystem 级别的权限,而普通 App 是不能使用这些权限的。
2.4 系统 App 能更轻松地实现进程保活
三方 App 为了不被杀掉,可以说是用尽了千方百计。保活对于系统 App 其实是非常简单的:
在 AndroidManifest.xml 中添加如下参数即可:
<application
android:persistent="true">3. 系统 App 添加依赖
1. 添加 AOSP 中已有的库
在 FirstSystemApp 的 Android.bp 中我们添加了很多依赖:
static_libs: ["androidx.appcompat_appcompat",
"com.google.android.material_material",
"androidx-constraintlayout_constraintlayout"],在 AOSP 中, 很多常用的库均以预编译模块的方式添加到系统源码中。比如常用的 AndroidX 库定义在 prebuilts/sdk/current/androidx 目录下。这些库通过 prebuilts/sdk/current/androidx/Android.bp 引入。比如 recyclerview 库的引入方式如下:
android_library {
name: "androidx.recyclerview_recyclerview",
sdk_version: "31",
apex_available: [
"//apex_available:platform",
"//apex_available:anyapex",
],
min_sdk_version: "14",
manifest: "manifests/androidx.recyclerview_recyclerview/AndroidManifest.xml",
static_libs: [
"androidx.recyclerview_recyclerview-nodeps",
"androidx.annotation_annotation",
"androidx.collection_collection",
"androidx.core_core",
"androidx.customview_customview",
],
java_version: "1.7",
}可以看到引入的是一个 android_library,名字叫 androidx.recyclerview_recyclerview。maifest 文件在 manifests/androidx.recyclerview_recyclerview/ 目录下,进入这个目录只有一个 AndroidManifest.xml 文件,其内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="androidx.recyclerview" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="14"
android:targetSdkVersion="28" />
</manifest>很奇怪,并没有看到 RecyclerView 库的源码,也没有看到 aar 库文件。我们接着看 Android.bp 中的依赖,其中一项是 androidx.recyclerview_recyclerview-nodeps,我们在 Android.bp 中看一下它的引入方式:
android_library_import {
name: "androidx.recyclerview_recyclerview-nodeps",
aars: ["m2repository/androidx/recyclerview/recyclerview/1.1.0-alpha07/recyclerview-1.1.0-alpha07.aar"],
sdk_version: "current",
min_sdk_version: "14",
static_libs: [
"androidx.annotation_annotation",
"androidx.collection_collection",
"androidx.core_core",
"androidx.customview_customview",
],
}这里看到了,它的 aar 库在这里: m2repository/androidx/recyclerview/recyclerview/1.1.0-alpha07/recyclerview-1.1.0-alpha07.aar
继续查阅我们可以发现,prebuilts/tools/common/m2 目录下引入了大量的三方库。
总结一下,当我们的系统 App 需要引入一个库的时候,通常会在 prebuilds 目录下查找:
- androidx 相关库引入,先在 prebuilts/sdk/current/androidx 下寻找配置好的 bp 文件
- 其他库引入,先在 prebuilts/tools/common/m2 下寻找寻找配置好的 bp 文件
都没有,就得自己引入了
2. 自己给 AOSP 添加库
2.1 java 库源码引入
这部分参考之前的文档添加 C/C++、Java 库
2.2 java 库以 jar 包形式引入
这部分参考之前的文档添加 C/C++、Java 库
2.3 Android 库源码引入
在 device/Jelly/Rice14 目录下创建如下的文件和文件夹

其中 MyCustomView.java 是一个用于演示的没有具体功能的自定义 View:
package com.yuandaima.firstsystemandroidlibrary;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
import androidx.annotation.Nullable;
public class MyCustomView extends View {
public MyCustomView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyCustomView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public MyCustomView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
public MyCustomView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
}AndroidManifest.xml 的内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.yuandaima.firstsystemandroidlibrary">
</manifest>Android.bp 的内容如下:
android_library {
name: "FirstSystemAndroidLibrary",
srcs: ["src/**/*.java"],
resource_dirs: ["res"],
manifest: "AndroidManifest.xml",
sdk_version: "current",
product_specific: true,
//依赖
static_libs: ["androidx.appcompat_appcompat",],
java_version: "1.7",
installable: true,
}接着修改我们的 FirstSystemApp 项目
Android.bp 添加依赖如下:
android_library {
//......
//依赖
static_libs: ["androidx.appcompat_appcompat",
"com.google.android.material_material",
"androidx-constraintlayout_constraintlayout",
"FirstSystemAndroidLibrary"],
}修改一下 MainActivity,在 App 里使用我们的自定义 View:
package com.yuandaima.firstsystemapp;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import com.yuandaima.firstsystemandroidlibrary.MyCustomView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
MyCustomView myView = new MyCustomView(this);
}
}接着编译系统,启动虚拟机,打开 app:
source build/envsetup.sh
lunch Rice14-eng
make -j16
emulator 这样我们的库就算引入完毕了。
2.4 Android 库以 aar 包形式引入
更多的时候 Android 库是以 aar 包的形式引入。
假设我们的 FirstSystemApp 需要引入 lottie 这个动画库。
首先我们这里下载好 lottie 库的 aar 打包文件。
在 device/Jelly/Rice14 目录下创建如下的目录结构:
liblottie/
├── Android.bp
└── lottie-5.2.0.aar其中 Android.bp 的内容如下:
android_library_import {
name: "lib-lottie",
aars: ["lottie-5.2.0.aar"],
sdk_version: "current",
}然后我们修改 FirstSystemApp 中的 Android.bp 引入这个库:
static_libs: ["androidx.appcompat_appcompat",
"com.google.android.material_material",
"androidx-constraintlayout_constraintlayout",
"FirstSystemAndroidLibrary",
"lib-lottie"],这样就可以在 App 中使用 lottie 库了
3. JNI 项目
3.1 创建 JNI 项目
Android 10 下,Android.bp(soong) 方式对 JNI 的支持有点问题,所以我们只有用 Android.mk 来演示了。Android 13 下 Android.bp (soong) 是完美支持 JNI 的。
在 device/Jelly/Rice14 目录下添加如下的文件与文件夹:
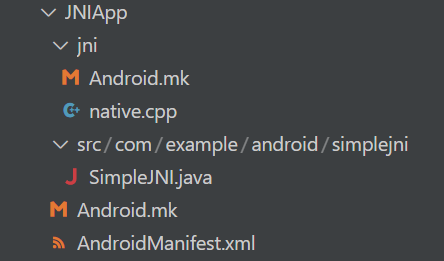
jni/Android.mk 内容如下:
LOCAL_PATH:= $(call my-dir)
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_MODULE_TAGS := optional
# This is the target being built.
LOCAL_MODULE:= myjnilib
# All of the source files that we will compile.
LOCAL_SRC_FILES:= \
native.cpp
# All of the shared libraries we link against.
LOCAL_LDLIBS := -llog
# No static libraries.
LOCAL_STATIC_LIBRARIES :=
LOCAL_CFLAGS := -Wall -Werror
LOCAL_NDK_STL_VARIANT := none
LOCAL_SDK_VERSION := current
LOCAL_PRODUCT_MODULE := true
include $(BUILD_SHARED_LIBRARY)jni/native.cpp 的内容如下:
/*
* Copyright (C) 2008 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
#define LOG_TAG "simplejni native.cpp"
#include <android/log.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "jni.h"
#define ALOGV(...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_VERBOSE, LOG_TAG, __VA_ARGS__)
#define ALOGD(...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, __VA_ARGS__)
#define ALOGI(...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO, LOG_TAG, __VA_ARGS__)
#define ALOGW(...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_WARN, LOG_TAG, __VA_ARGS__)
#define ALOGE(...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_ERROR, LOG_TAG, __VA_ARGS__)
static jint
add(JNIEnv* /*env*/, jobject /*thiz*/, jint a, jint b) {
int result = a + b;
ALOGI("%d + %d = %d", a, b, result);
return result;
}
static const char *classPathName = "com/example/android/simplejni/Native";
static JNINativeMethod methods[] = {
{"add", "(II)I", (void*)add },
};
/*
* Register several native methods for one class.
*/
static int registerNativeMethods(JNIEnv* env, const char* className,
JNINativeMethod* gMethods, int numMethods)
{
jclass clazz;
clazz = env->FindClass(className);
if (clazz == NULL) {
ALOGE("Native registration unable to find class '%s'", className);
return JNI_FALSE;
}
if (env->RegisterNatives(clazz, gMethods, numMethods) < 0) {
ALOGE("RegisterNatives failed for '%s'", className);
return JNI_FALSE;
}
return JNI_TRUE;
}
/*
* Register native methods for all classes we know about.
*
* returns JNI_TRUE on success.
*/
static int registerNatives(JNIEnv* env)
{
if (!registerNativeMethods(env, classPathName,
methods, sizeof(methods) / sizeof(methods[0]))) {
return JNI_FALSE;
}
return JNI_TRUE;
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
/*
* This is called by the VM when the shared library is first loaded.
*/
typedef union {
JNIEnv* env;
void* venv;
} UnionJNIEnvToVoid;
jint JNI_OnLoad(JavaVM* vm, void* /*reserved*/)
{
UnionJNIEnvToVoid uenv;
uenv.venv = NULL;
jint result = -1;
JNIEnv* env = NULL;
ALOGI("JNI_OnLoad");
if (vm->GetEnv(&uenv.venv, JNI_VERSION_1_4) != JNI_OK) {
ALOGE("ERROR: GetEnv failed");
goto bail;
}
env = uenv.env;
if (registerNatives(env) != JNI_TRUE) {
ALOGE("ERROR: registerNatives failed");
goto bail;
}
result = JNI_VERSION_1_4;
bail:
return result;
}SimpleJNI.java 的内容如下:
package com.example.android.simplejni;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class SimpleJNI extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
TextView tv = new TextView(this);
int sum = Native.add(2, 3);
tv.setText("2 + 3 = " + Integer.toString(sum));
setContentView(tv);
}
}
class Native {
static {
// The runtime will add "lib" on the front and ".o" on the end of
// the name supplied to loadLibrary.
System.loadLibrary("simplejni");
}
static native int add(int a, int b);
}最外面的 Android.mk 的内容如下:
TOP_LOCAL_PATH:= $(call my-dir)
# Build activity
LOCAL_PATH:= $(TOP_LOCAL_PATH)
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_MODULE_TAGS := optional
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := $(call all-subdir-java-files)
LOCAL_PACKAGE_NAME := JNIApp
LOCAL_JNI_SHARED_LIBRARIES := myjnilib
LOCAL_PROGUARD_ENABLED := disabled
LOCAL_SDK_VERSION := current
LOCAL_DEX_PREOPT := false
LOCAL_PRODUCT_MODULE := true
include $(BUILD_PACKAGE)
# ============================================================
# Also build all of the sub-targets under this one: the shared library.
include $(call all-makefiles-under,$(LOCAL_PATH))AndroidManifest.xml 的内容如下:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.android.simplejni">
<application android:label="Simple JNI">
<activity android:name="SimpleJNI">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest> 最后在 device/Jelly/Rice14/Rice14.mk 中添加:
PRODUCT_PACKAGES += helloworld \
JNIApp \编译并运行虚拟机就可以看到 JNIApp 了:

3.2 JNIApp 链接自定义库
我们这里尝试修改 JNIApp,让其引用到我们的 libmymath 库。
修改 JNIApp/jni/Android.mk:
# 添加以下内容
LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES := libmymath修改 JNIApp/jni/native.cpp:
#include "my_math.h"
static jint
add(JNIEnv* /*env*/, jobject /*thiz*/, jint a, jint b) {
int result = a + b;
result = my_add(result, result);
ALOGI("%d + %d = %d", a, b, result);
return result;
}然后编译系统,发现报以下错误:
error: myjnilib (native:ndk:none:none) should not link to libmymath (native:platform)可以看出是编译平台不一致导致的,修改 JNIApp/jni/Android.mk:
# 下面这行注释掉即可
# LOCAL_SDK_VERSION := current最后重新编译,执行虚拟机即可
参考资料
- android系统源码中添加app源码(源码部署移植)
- AOSP 预置 APP
- Android Framework 常见解决方案(15)android内置可卸载APP集成方案
- Android Framework 常见解决方案(02)android系统级APP集成方案
- 在AOSP编译时,添加预编译apk
- Android系统预制可自由卸载apk
- Soong Modules Reference
- Jetpack太香了,系统App也想用,怎么办?
- Android.bp 文件中引入aar、jar、so库正确编译方法(值得收藏)
- Jetpack太香了,系统App也想用,怎么办?
- AOSP: Creating a System Application
1、本站所有资源均从互联网上收集整理而来,仅供学习交流之用,因此不包含技术服务请大家谅解!
2、本站不提供任何实质性的付费和支付资源,所有需要积分下载的资源均为网站运营赞助费用或者线下劳务费用!
3、本站所有资源仅用于学习及研究使用,您必须在下载后的24小时内删除所下载资源,切勿用于商业用途,否则由此引发的法律纠纷及连带责任本站和发布者概不承担!
4、本站站内提供的所有可下载资源,本站保证未做任何负面改动(不包含修复bug和完善功能等正面优化或二次开发),但本站不保证资源的准确性、安全性和完整性,用户下载后自行斟酌,我们以交流学习为目的,并不是所有的源码都100%无错或无bug!如有链接无法下载、失效或广告,请联系客服处理!
5、本站资源除标明原创外均来自网络整理,版权归原作者或本站特约原创作者所有,如侵犯到您的合法权益,请立即告知本站,本站将及时予与删除并致以最深的歉意!
6、如果您也有好的资源或教程,您可以投稿发布,成功分享后有站币奖励和额外收入!
7、如果您喜欢该资源,请支持官方正版资源,以得到更好的正版服务!
8、请您认真阅读上述内容,注册本站用户或下载本站资源即您同意上述内容!
原文链接:https://www.dandroid.cn/archives/20505,转载请注明出处。


评论0