1 简介
WorkManager是Jetpack组件库中的一个组件,主要用于处理立即执行、长时间运行、可延迟执行的并且保证必须执行的后台操作任务。例如上传日志,定时上传数据,定时下载数据,定时备份数据等等。即使APP退出或者进程被杀,任务依旧可以执行,不过需要注意的是目前WorkManager在Google Pixel手机上可以完美使用,但是在其他品牌手机使用有一定的问题。
WorkManager可处理的3种永久性工作:
- 立即执行:必须立即开始且很快就完成的任务。
- 长时间运行:运行时间可能较长(有可能超过10分钟)的任务。
- 可延期执行:延期开始并且可以定期运行的预定任务。
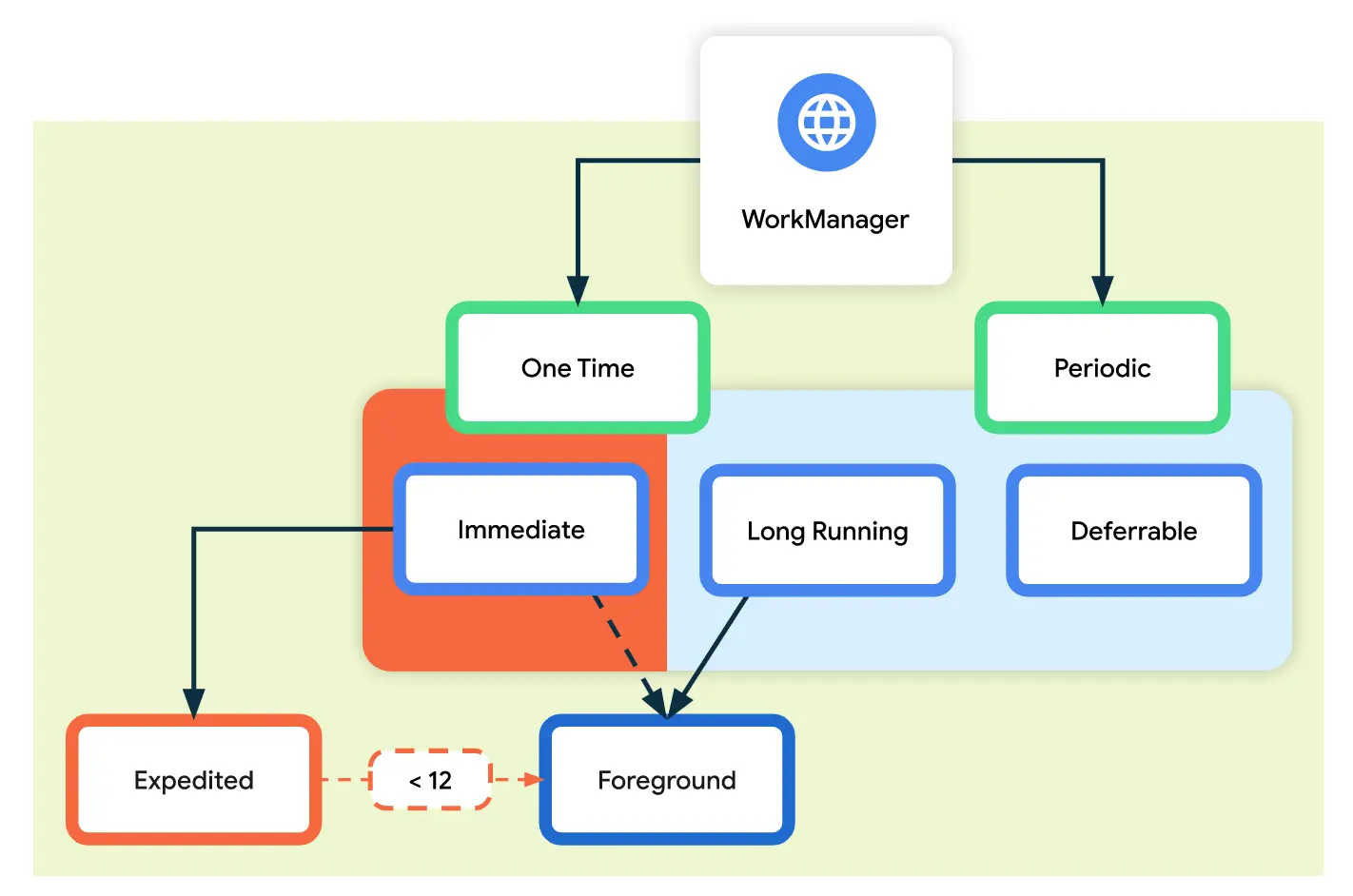
| 类型 | 周期 | 使用方式 |
|---|---|---|
| 立即 | 一次性 | OneTimeWorkRequest 和 Worker。如需处理加急工作,请对 OneTimeWorkRequest 调用 setExpedited()。 |
| 长期运行 | 一次性或定期 | 任意 WorkRequest 或 Worker。在工作器中调用 setForeground() 来处理通知。 |
| 可延期 | 一次性或定期 | PeriodicWorkRequest 和 Worker。 |
Google Developer文档:https://developer.android.google.cn/topic/libraries/architecture/workmanager
原理:
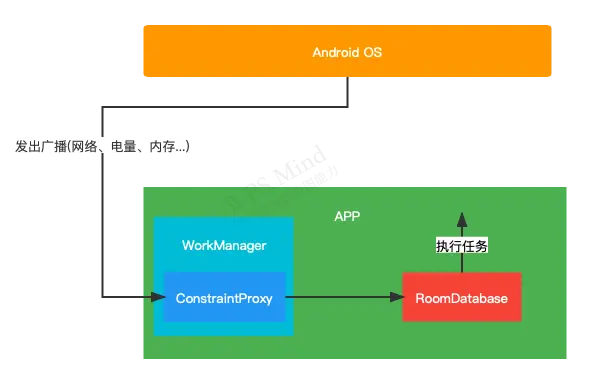
WorkManager引入后,使用Room将任务存入数据库,然后使用系统服务区执行这些任务,这样就实现了即使APP集成被杀,APP被强制退出的时候,任务依然能被执行。同时WorkManager会在AndroidManifest.xml中注册receiver和service,用来接收系统系统的广播,比如网络状态、低电量、低内存、手机空闲等,来执行附带约束的任务。
2 使用
2.1 添加依赖
dependencies {
//WorkManager依赖
def work_version = "2.7.1"
implementation "androidx.work:work-runtime:$work_version"
...
}
示例代码使用了ViewBinding,需要开启ViewBinding。
android{
...
//开启ViewBinding
viewBinding {
enabled = true
}
}
2.2 创建Activity
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var binding: ActivityMainBinding
@RequiresApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.M)
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
setContentView(binding.root)
initView()
}
@RequiresApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.M)
private fun initView() {
...
}
}
XML中有几个按钮测试对应的后台任务。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="2dp"
android:text="执行单次后台任务"
android:textAllCaps="false" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="2dp"
android:text="执行单次后台任务-发送数据"
android:textAllCaps="false" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="2dp"
android:text="执行多个后台任务-按顺序"
android:textAllCaps="false" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="2dp"
android:text="执行多个后台任务-集合形式"
android:textAllCaps="false" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button5"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="2dp"
android:text="周期性重复执行后台任务"
android:textAllCaps="false" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button6"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="2dp"
android:text="附带约束条件执行后台任务"
android:textAllCaps="false" />
</LinearLayout>2.3 功能测试
2.3.1 执行单次后台任务
创建SimpleWorker,继承Worker,实现dowWork()方法,dowWork()是一个异步方法,它是在Runnable的run方法中调用的。doWork()返回的Result会通知 WorkManager服务工作是否成功,以及工作失败时是否应重试工作。
Result有3种:
Result.success():工作成功完成。Result.failure():工作失败。Result.retry():工作失败,应根据其重试政策在其他时间尝试。
class SimpleWorker(context: Context, workParams: WorkerParameters) :
Worker(context, workParams) {
companion object {
const val TAG = "---SimpleWorker"
}
/**
* doWork() 返回的 Result 会通知 WorkManager 服务工作是否成功,以及工作失败时是否应重试工作。
* Result.success():工作成功完成。
* Result.failure():工作失败。
* Result.retry():工作失败,应根据其重试政策在其他时间尝试。
*
* 这是一个后台任务,是异步的,在Runnable中执行。
*/
override fun doWork(): Result {
Log.d(TAG, "doWork: work start...")
try {
Thread.sleep(3000)
} catch (e: IOException) {
e.printStackTrace()
return Result.failure()
} finally {
Log.d(TAG, "doWork: work end...")
}
return Result.success()
}
}
在MainActivity的initView()方法中执行该单次任务。
步骤:
1、构建OneTimeWorkRequest。
2、调用WorkManager.getInstance(this).enqueue()提交任务到队列。
//单次后台任务
binding.button1.setOnClickListener {
//构建WorkRequest
val oneTimeWorkRequest =
OneTimeWorkRequest.Builder(SimpleWorker::class.java).build()
//调用enqueue()方法将WorkRequest提交到WorkManager任务队列中
WorkManager.getInstance(this).enqueue(oneTimeWorkRequest)
//取消任务
//取消所有任务
WorkManager.getInstance(this).cancelAllWork()
//取消指定任务
WorkManager.getInstance(this).cancelWorkById(oneTimeWorkRequest.id)
}
2.3.2 执行单次后台任务-传递数据
WorkManager在执行任务的时候,可以携带数据交给Worker,Worker中可以接收该数据,然后在doWork()的返回结果中也可以返回数据给WorkManager,WorkManager可以通过LiveData去接收返回的数据。
创建SimpleDataWorker类:
class SimpleDataWorker(context: Context, private val workParams: WorkerParameters) :
Worker(context, workParams) {
companion object {
const val TAG = "---SimpleDataWorker"
}
override fun doWork(): Result {
Log.d(TAG, "doWork: work start...")
//接收MainActivity中传过来的数据
val inputData = workParams.inputData.getString("inputData")
Log.d(TAG, "doWork: receive data:$inputData")
//将数据再返回给MainActivity
val outputData = Data.Builder().putString("outputData", "Tree New Bee").build()
return Result.success(outputData)
}
}
在MainActivity的initView()方法中执行该任务。
步骤:
1、使用Data.Builder()构造要传递的数据体。
2、构造OneTimeWorkRequest。
3、用WorkManager.getInstance(this).getWorkInfoByIdLiveData(oneTimeWorkRequest.id).observe(this){}来获取LiveData去监听状态和数据变化。
4、调用WorkManager.getInstance(this).enqueue()提交任务到队列。
//执行单次后台任务-传递数据
binding.button2.setOnClickListener {
//要发传递出去的数据
val inputData = Data.Builder().putString("inputData", "New Bee").build()
//构建WorkRequest
val oneTimeWorkRequest = OneTimeWorkRequest.Builder(SimpleDataWorker::class.java)
.setInputData(inputData).build()//设置要传递的数据
//通过LiveData接收BackgroundWorker2返回的数据
WorkManager.getInstance(this).getWorkInfoByIdLiveData(oneTimeWorkRequest.id)
.observe(this) {
//RUNNING时,outputData为null;SUCCEEDED时,才能获取到数据。
Log.d(
SimpleDataWorker.TAG,
"state 1: ${it.state} outputData:${it.outputData.getString("outputData")}"
)
//当状态处于完成时,也就是SUCCEEDED、FAILED、CANCELLED时,任务才结束,才能去拿结果数据,不然获取到的数据是null
if (it.state.isFinished) {
Log.d(
SimpleDataWorker.TAG,
"state 2: ${it.state} outputData:${it.outputData.getString("outputData")}"
)
}
}
//提交任务,任务加入队列
WorkManager.getInstance(this).enqueue(oneTimeWorkRequest)
}
getWorkInfoByIdLiveData方法会回调一个WorkInfo对象,WorkInfo中包含状态和Worker返回的数据。
只要当状态是SUCCEEDED、FAILED、CANCELLED这3个的时候,才表示任务结束,这时候才能去获取数据,其他状态获取到的数据是null。
2.3.3 执行多个后台任务-按顺序
先创建3个任务:
class OrderWorker1(context: Context, workParams: WorkerParameters) :
Worker(context, workParams) {
companion object {
private const val TAG = "---OrderWorker1"
}
override fun doWork(): Result {
Log.d(TAG, "doWork: start...")
return Result.success()
}
}
class OrderWorker2(context: Context, workParams: WorkerParameters) :
Worker(context, workParams) {
companion object {
private const val TAG = "---OrderWorker2"
}
override fun doWork(): Result {
Log.d(TAG, "doWork: start...")
return Result.success()
}
}
class OrderWorker3(context: Context, workParams: WorkerParameters) :
Worker(context, workParams) {
companion object {
private const val TAG = "---OrderWorker3"
}
override fun doWork(): Result {
Log.d(TAG, "doWork: start...")
return Result.success()
}
}
然后按顺序执行这3个任务,核心方法是beginWith()和then(),beginWith()可以做一些前置工作,比如初始化等等,then()中可以做一些后续工作。只有当前一个任务执行成功才会执行下一个任务。
//执行多个后台任务-按顺序
binding.button3.setOnClickListener {
val oneTimeWorkRequest1 =
OneTimeWorkRequest.Builder(OrderWorker1::class.java).build()
val oneTimeWorkRequest2 =
OneTimeWorkRequest.Builder(OrderWorker2::class.java).build()
val oneTimeWorkRequest3 =
OneTimeWorkRequest.Builder(OrderWorker3::class.java).build()
//按顺序执行1,2,3
WorkManager.getInstance(this)
.beginWith(oneTimeWorkRequest1)
.then(oneTimeWorkRequest2)
.then(oneTimeWorkRequest3)
.enqueue()
}
2.3.4 执行多个后台任务-集合方式
集合方式和2.3.3中按顺序执行没有什么大的区别,只不过是把多个任务放在集合中,然后再交给WorkManager,同样可以控制顺序。
//执行多个后台任务-集合方式
binding.button4.setOnClickListener {
val oneTimeWorkRequest1 =
OneTimeWorkRequest.Builder(OrderWorker1::class.java).build()
val oneTimeWorkRequest2 =
OneTimeWorkRequest.Builder(OrderWorker2::class.java).build()
val oneTimeWorkRequest3 =
OneTimeWorkRequest.Builder(OrderWorker3::class.java).build()
val oneTimeWorkRequests = mutableListOf()
oneTimeWorkRequests.add(oneTimeWorkRequest2)
oneTimeWorkRequests.add(oneTimeWorkRequest3)
//先执行2,3,再执行1
WorkManager.getInstance(this).beginWith(oneTimeWorkRequests)
.then(oneTimeWorkRequest1)
.enqueue()
}
2.3.5 周期性重复执行后台任务
周期性重复执行任务就可以实现类似日志上传的功能,WorkManager要求的任务重复周期不能小于15分钟。
周期任务的WorkRequest对象是PeriodicWorkRequest。
//周期性重复执行后台任务
binding.button5.setOnClickListener {
//重复周期最少设置15分钟,少于15分钟编译器会报错
val periodicWorkRequest =
PeriodicWorkRequest.Builder(SimpleWorker::class.java, 15, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.build()
//监听状态和数据变化
WorkManager.getInstance(this).getWorkInfoByIdLiveData(periodicWorkRequest.id)
.observe(this) {
Log.d(SimpleWorker.TAG, "state: ${it.state}")
if (it.state.isFinished) {
Log.d(SimpleWorker.TAG, "work finished...")
}
}
//提交任务,任务加入队列
WorkManager.getInstance(this).enqueue(periodicWorkRequest)
}
2.3.6 附带约束条件执行后台任务
附带约束条件的任务是为了对APP性能进行优化,比如该任务只在联网的时候才能进行,只有在充电的时候才能进行,只有在空闲时期(没有其他大量服务在运行)的时候才能进行,这样就能降低APP功耗,充分利用手机性能。
//附带约束条件执行后台任务
binding.button6.setOnClickListener {
//约束条件
val constraints = Constraints.Builder()
.setRequiredNetworkType(NetworkType.CONNECTED)//联网中
.setRequiresCharging(true)//充电中
.setRequiresBatteryNotLow(true)//非低电量
// .setRequiresDeviceIdle(true)//手机空闲中
.setRequiresStorageNotLow(true)//非低内存
.build()
val oneTimeWorkRequest = OneTimeWorkRequest.Builder(SimpleWorker::class.java)
.setConstraints(constraints)//设置约束
.build()
//提交任务,任务加入队列
WorkManager.getInstance(this).enqueue(oneTimeWorkRequest)
}
完整源码可以在公号【木水Code】发送”WorkManager”进行下载。
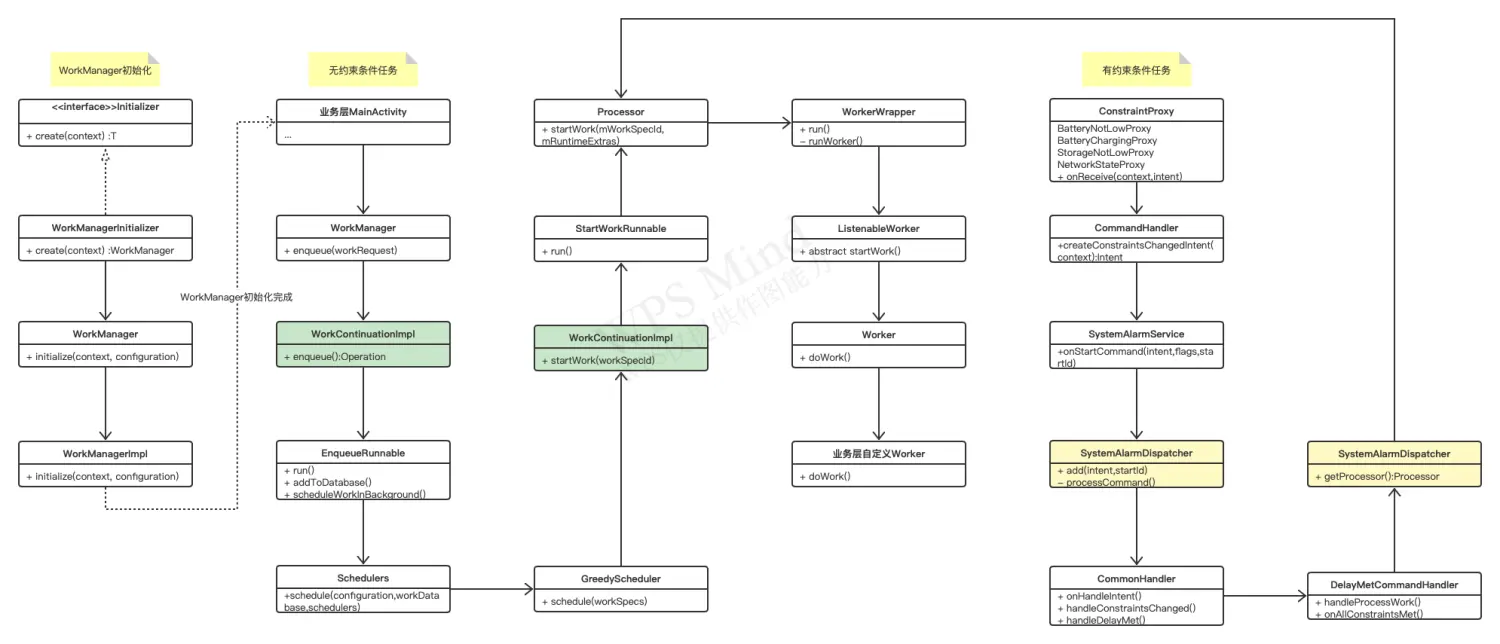
3 源码流程图
源码流程分析主要分三部分:
- WorkManager初始化过程
- WorkManager执行无约束条件的任务
- WorkManager执行有约束条件的任务
阅读源码的过程中结合该流程图,能更加快速理解,加深记忆。
4 源码分析
4.1 WorkManager初始化
在MainActivity中,调用了WorkManager.getInstance(this)。
public static @NonNull WorkManager getInstance(@NonNull Context context) {
return WorkManagerImpl.getInstance(context);
}
然后又调用了WorkManager的子类WorkManagerImpl.getInstance()方法去初始化。
@RestrictTo(RestrictTo.Scope.LIBRARY_GROUP)
public static @NonNull WorkManagerImpl getInstance(@NonNull Context context) {
synchronized (sLock) {
WorkManagerImpl instance = getInstance();
if (instance == null) {
Context appContext = context.getApplicationContext();
if (appContext instanceof Configuration.Provider) {
//初始化
initialize(
appContext,
((Configuration.Provider) appContext).getWorkManagerConfiguration());
instance = getInstance(appContext);
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("WorkManager is not initialized properly. You "
+ "have explicitly disabled WorkManagerInitializer in your manifest, "
+ "have not manually called WorkManager#initialize at this point, and "
+ "your Application does not implement Configuration.Provider.");
}
}
return instance;
}
}
WorkManagerImpl.getInstance()又调用了WorkManagerImpl.initialize()去实例化WorkManagerImpl。
@RestrictTo(RestrictTo.Scope.LIBRARY_GROUP)
public static void initialize(@NonNull Context context, @NonNull Configuration configuration) {
synchronized (sLock) {
if (sDelegatedInstance != null && sDefaultInstance != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("WorkManager is already initialized. Did you "
+ "try to initialize it manually without disabling "
+ "WorkManagerInitializer? See "
+ "WorkManager#initialize(Context, Configuration) or the class level "
+ "Javadoc for more information.");
}
if (sDelegatedInstance == null) {
context = context.getApplicationContext();
if (sDefaultInstance == null) {
sDefaultInstance = new WorkManagerImpl(
context,
configuration,
new WorkManagerTaskExecutor(configuration.getTaskExecutor()));
}
sDelegatedInstance = sDefaultInstance;
}
}
}
但是这里并不是第一次初始化。
反编译或者直接用AndroidStudio打开APK,点开AndroidManifest.xml文件,能看到引入WorkManager之后生成了一个provider,在这个InitializationProvider中,有一个WorkManagerInitializer。
<provider
android:name="androidx.startup.InitializationProvider"
android:exported="false"
android:authorities="cn.zhangmushui.workmanagersample.androidx-startup">
<meta-data
android:name="androidx.work.WorkManagerInitializer"
android:value="androidx.startup" />
</provider>进入WorkManagerInitializer:
public final class WorkManagerInitializer implements Initializer {
private static final String TAG = Logger.tagWithPrefix("WrkMgrInitializer");
@NonNull
@Override
public WorkManager create(@NonNull Context context) {
// Initialize WorkManager with the default configuration.
Logger.get().debug(TAG, "Initializing WorkManager with default configuration.");
//WorkManager的初始化工作
WorkManager.initialize(context, new Configuration.Builder().build());
return WorkManager.getInstance(context);
}
@NonNull
@Override
public List>> dependencies() {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
}
然后调用了WorkManager.initialize()。
public static void initialize(@NonNull Context context, @NonNull Configuration configuration) {
WorkManagerImpl.initialize(context, configuration);
}
WorkManager.initialize()调用了WorkManagerImpl.initialize(),真正的初始化工作就在这里进行。最终和MainActivity中调用WorkManager.getInstance(this)一样,走到了WorkManagerImpl.initialize()。所以,AndroidManifest.xml中的provider才是WorkManager的第一次实例化。
@RestrictTo(RestrictTo.Scope.LIBRARY_GROUP)
public static void initialize(@NonNull Context context, @NonNull Configuration configuration) {
synchronized (sLock) {
if (sDelegatedInstance != null && sDefaultInstance != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("WorkManager is already initialized. Did you "
+ "try to initialize it manually without disabling "
+ "WorkManagerInitializer? See "
+ "WorkManager#initialize(Context, Configuration) or the class level "
+ "Javadoc for more information.");
}
if (sDelegatedInstance == null) {
context = context.getApplicationContext();
if (sDefaultInstance == null) {
//实例化WorkManager
sDefaultInstance = new WorkManagerImpl(
context,
configuration,
//实例化WorkManagerTaskExecutor
new WorkManagerTaskExecutor(configuration.getTaskExecutor()));
}
sDelegatedInstance = sDefaultInstance;
}
}
}
WorkManager初始化的时候会传入一个默认Configuration,Configuration中包含了任务调度器,任务执行器等对象。
在initialize方法中,实例化了一个WorkManagerTaskExecutor传入WorkManagerImpl的构造方法,用来执行任务。
@RestrictTo(RestrictTo.Scope.LIBRARY_GROUP)
public WorkManagerImpl(
@NonNull Context context,
@NonNull Configuration configuration,
@NonNull TaskExecutor workTaskExecutor) {
this(context,
configuration,
workTaskExecutor,
context.getResources().getBoolean(R.bool.workmanager_test_configuration));
}
@RestrictTo(RestrictTo.Scope.LIBRARY_GROUP)
public WorkManagerImpl(
@NonNull Context context,
@NonNull Configuration configuration,
@NonNull TaskExecutor workTaskExecutor,
boolean useTestDatabase) {
this(context,
configuration,
workTaskExecutor,
WorkDatabase.create(
context.getApplicationContext(),
workTaskExecutor.getBackgroundExecutor(),
useTestDatabase)
);
}
@RestrictTo(RestrictTo.Scope.LIBRARY_GROUP)
public WorkManagerImpl(
@NonNull Context context,
@NonNull Configuration configuration,
@NonNull TaskExecutor workTaskExecutor,
@NonNull WorkDatabase database) {
Context applicationContext = context.getApplicationContext();
Logger.setLogger(new Logger.LogcatLogger(configuration.getMinimumLoggingLevel()));
//创建调度器Scheduler
List schedulers =
createSchedulers(applicationContext, configuration, workTaskExecutor);
//实例化处理器Processor,处理器可以根据需要智能的去调度和执行任务。
Processor processor = new Processor(
context,
configuration,
workTaskExecutor,
database,
schedulers);
//真正的初始化
internalInit(context, configuration, workTaskExecutor, database, schedulers, processor);
}
在最后一个调用的构造方法中,首先创建了一个调度器Scheduler用于任务调度:
@RestrictTo(RestrictTo.Scope.LIBRARY_GROUP)
@NonNull
public List createSchedulers(
@NonNull Context context,
@NonNull Configuration configuration,
@NonNull TaskExecutor taskExecutor) {
return Arrays.asList(
Schedulers.createBestAvailableBackgroundScheduler(context, this),
// Specify the task executor directly here as this happens before internalInit.
// GreedyScheduler creates ConstraintTrackers and controllers eagerly.
//贪婪调度器
new GreedyScheduler(context, configuration, taskExecutor, this));
}
接着实例化了一个Processor,处理器可以根据需要智能的去调度和执行任务。
Processor processor = new Processor(
context,
configuration,
workTaskExecutor,
database,
schedulers);
最后调用internalInit进行真正的初始化工作。
private void internalInit(@NonNull Context context,
@NonNull Configuration configuration,
@NonNull TaskExecutor workTaskExecutor,
@NonNull WorkDatabase workDatabase,
@NonNull List schedulers,
@NonNull Processor processor) {
context = context.getApplicationContext();
mContext = context;
mConfiguration = configuration;
mWorkTaskExecutor = workTaskExecutor;
mWorkDatabase = workDatabase;
mSchedulers = schedulers;
mProcessor = processor;
mPreferenceUtils = new PreferenceUtils(workDatabase);
mForceStopRunnableCompleted = false;
// Check for direct boot mode
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.N && context.isDeviceProtectedStorage()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot initialize WorkManager in direct boot mode");
}
// Checks for app force stops.
//检查app强制停止
mWorkTaskExecutor.executeOnBackgroundThread(new ForceStopRunnable(context, this));
}
executeOnBackgroundThread方法传入了一个ForceStopRunnable对象,在这里,检查到app正在执行任务的时候,发生了闪退崩溃退出了程序,或者手机关机,就会重试之前的任务。
在WorkManager初始化的过程中,ForceStopRunnable的run方法中,会检测app被强制停止运行之前是否还有未完成的任务,如果有,会继续执行。
@Override
public void run() {
try {
if (!multiProcessChecks()) {
return;
}
while (true) {
// Migrate the database to the no-backup directory if necessary.
WorkDatabasePathHelper.migrateDatabase(mContext);
// Clean invalid jobs attributed to WorkManager, and Workers that might have been
// interrupted because the application crashed (RUNNING state).
Logger.get().debug(TAG, "Performing cleanup operations.");
try {
forceStopRunnable();
break;
} catch (SQLiteCantOpenDatabaseException
| SQLiteDatabaseCorruptException
| SQLiteDatabaseLockedException
| SQLiteTableLockedException
| SQLiteConstraintException
| SQLiteAccessPermException exception) {
mRetryCount++;
if (mRetryCount >= MAX_ATTEMPTS) {
// ForceStopRunnable is usually the first thing that accesses a database
// (or an app's internal data directory). This means that weird
// PackageManager bugs are attributed to ForceStopRunnable, which is
// unfortunate. This gives the developer a better error
// message.
String message = "The file system on the device is in a bad state. "
+ "WorkManager cannot access the app's internal data store.";
Logger.get().error(TAG, message, exception);
IllegalStateException throwable = new IllegalStateException(message,
exception);
InitializationExceptionHandler exceptionHandler =
mWorkManager.getConfiguration().getExceptionHandler();
if (exceptionHandler != null) {
Logger.get().debug(TAG,
"Routing exception to the specified exception handler",
throwable);
exceptionHandler.handleException(throwable);
break;
} else {
throw throwable;
}
} else {
long duration = mRetryCount * BACKOFF_DURATION_MS;
Logger.get()
.debug(TAG, String.format("Retrying after %s", duration),
exception);
sleep(mRetryCount * BACKOFF_DURATION_MS);
}
}
}
} finally {
mWorkManager.onForceStopRunnableCompleted();
}
}
WorkManager初始化过程总结:
- WorkManager的真正初始化是由ContentProvider提供的WorkManagerInitializer中执行的,最终的实现是在WorkManager的子类WorkManagerImpl中。
- 初始化的过程中实例化了Configuration、WorkManagerTaskExecutor、WorkDatabase、GreedyScheduler、Processor。
- 会检测APP发生强制退出之前是否有未完成的任务,如果有,会继续执行。
4.2 WorkManager无约束条件任务的执行
在MainActivity中,调用了enqueue():
WorkManager.getInstance(this).enqueue()
进入WorkManager:
@NonNull
public final Operation enqueue(@NonNull WorkRequest workRequest) {
return enqueue(Collections.singletonList(workRequest));
}
调用WorkManager的抽象方法enqueue:
@NonNull
public abstract Operation enqueue(@NonNull List extends WorkRequest> requests);
该抽象方法在WorkManagerImpl中实现:
public Operation enqueue(
@NonNull List extends WorkRequest> requests) {
// This error is not being propagated as part of the Operation, as we want the
// app to crash during development. Having no workRequests is always a developer error.
if (requests.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"enqueue needs at least one WorkRequest.");
}
return new WorkContinuationImpl(this, requests).enqueue();
}
实例化了一个WorkContinuationImpl对象,然后调用WorkContinuationImpl的enqueue方法。WorkContinuationImpl继承了WorkContinuation:
public WorkContinuationImpl(
@NonNull WorkManagerImpl workManagerImpl,
@NonNull List extends WorkRequest> work) {
this(
workManagerImpl,
null,
ExistingWorkPolicy.KEEP,
work,
null);
}
WorkContinuation保存了任务相关的一些信息:
public WorkContinuationImpl(@NonNull WorkManagerImpl workManagerImpl,
@Nullable String name,
@NonNull ExistingWorkPolicy existingWorkPolicy,
@NonNull List extends WorkRequest> work,
@Nullable List parents) {
mWorkManagerImpl = workManagerImpl;
mName = name;
mExistingWorkPolicy = existingWorkPolicy;
mWork = work;
mParents = parents;
mIds = new ArrayList<>(mWork.size());
mAllIds = new ArrayList<>();
if (parents != null) {
for (WorkContinuationImpl parent : parents) {
mAllIds.addAll(parent.mAllIds);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < work.size(); i++) {
String id = work.get(i).getStringId();
mIds.add(id);
mAllIds.add(id);
}
}
在WorkContinuationImpl的enqueue方法中,WorkManagerImpl中的TaskExecutor执行了EnqueueRunnable:
@Override
public @NonNull Operation enqueue() {
// Only enqueue if not already enqueued.
if (!mEnqueued) {
// The runnable walks the hierarchy of the continuations
// and marks them enqueued using the markEnqueued() method, parent first.
EnqueueRunnable runnable = new EnqueueRunnable(this);
//TaskExecutor执行EnqueueRunnable
mWorkManagerImpl.getWorkTaskExecutor().executeOnBackgroundThread(runnable);
mOperation = runnable.getOperation();
} else {
Logger.get().warning(TAG,
String.format("Already enqueued work ids (%s)", TextUtils.join(", ", mIds)));
}
return mOperation;
}
EnqueueRunnable中的run()方法如下所示,调用了scheduleWorkInBackground(),这是后台执行任务的核心方法:
@Override
public void run() {
try {
if (mWorkContinuation.hasCycles()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
String.format("WorkContinuation has cycles (%s)", mWorkContinuation));
}
boolean needsScheduling = addToDatabase();
if (needsScheduling) {
// Enable RescheduleReceiver, only when there are Worker's that need scheduling.
final Context context =
mWorkContinuation.getWorkManagerImpl().getApplicationContext();
PackageManagerHelper.setComponentEnabled(context, RescheduleReceiver.class, true);
//在后台执行任务
scheduleWorkInBackground();
}
mOperation.setState(Operation.SUCCESS);
} catch (Throwable exception) {
mOperation.setState(new Operation.State.FAILURE(exception));
}
}
scheduleWorkInBackground()方法如下所示:
@VisibleForTesting
public void scheduleWorkInBackground() {
WorkManagerImpl workManager = mWorkContinuation.getWorkManagerImpl();
//调用Schedulers.schedule(),传入了Configuration、WorkDatabase、Scheduler
Schedulers.schedule(
workManager.getConfiguration(),
workManager.getWorkDatabase(),
workManager.getSchedulers());
}
调用Schedulers.schedule(),传入了Configuration、WorkDatabase、Scheduler:
public static void schedule(
...
if (eligibleWorkSpecsForLimitedSlots != null
&& eligibleWorkSpecsForLimitedSlots.size() > 0) {
WorkSpec[] eligibleWorkSpecsArray =
new WorkSpec[eligibleWorkSpecsForLimitedSlots.size()];
eligibleWorkSpecsArray =
eligibleWorkSpecsForLimitedSlots.toArray(eligibleWorkSpecsArray);
//遍历每个任务进行处理,由于这里执行的是没有限制条件的任务
//所以最终调用的是贪婪调度器GreedyScheduler的schedule方法
for (Scheduler scheduler : schedulers) {
if (scheduler.hasLimitedSchedulingSlots()) {
scheduler.schedule(eligibleWorkSpecsArray);
}
}
}
...
}
遍历每个任务去执行,没有约束条件的任务最终是调用了贪婪调度器GreedyScheduler.schedule()执行:
@Override
public void schedule(@NonNull WorkSpec... workSpecs) {
...
Set constrainedWorkSpecs = new HashSet<>();
Set constrainedWorkSpecIds = new HashSet<>();
for (WorkSpec workSpec : workSpecs) {
long nextRunTime = workSpec.calculateNextRunTime();
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (workSpec.state == WorkInfo.State.ENQUEUED) {
if (now < nextRunTime) {
// Future work
if (mDelayedWorkTracker != null) {
mDelayedWorkTracker.schedule(workSpec);
}
} else if (workSpec.hasConstraints()) {
if (SDK_INT >= 23 && workSpec.constraints.requiresDeviceIdle()) {
// Ignore requests that have an idle mode constraint.
Logger.get().debug(TAG,
String.format("Ignoring WorkSpec %s, Requires device idle.",
workSpec));
} else if (SDK_INT >= 24 && workSpec.constraints.hasContentUriTriggers()) {
// Ignore requests that have content uri triggers.
Logger.get().debug(TAG,
String.format("Ignoring WorkSpec %s, Requires ContentUri triggers.",
workSpec));
} else {
constrainedWorkSpecs.add(workSpec);
constrainedWorkSpecIds.add(workSpec.id);
}
} else {
Logger.get().debug(TAG, String.format("Starting work for %s", workSpec.id));
//无约束条件会直接走这里
mWorkManagerImpl.startWork(workSpec.id);
}
}
}
...
}
没有约束条件,直接走到了WorkManagerImpl.startWork():
@RestrictTo(RestrictTo.Scope.LIBRARY_GROUP)
public void startWork(@NonNull String workSpecId) {
startWork(workSpecId, null);
}
@RestrictTo(RestrictTo.Scope.LIBRARY_GROUP)
public void startWork(
@NonNull String workSpecId,
@Nullable WorkerParameters.RuntimeExtras runtimeExtras) {
mWorkTaskExecutor
.executeOnBackgroundThread(
new StartWorkRunnable(this, workSpecId, runtimeExtras));
}
进入StartWorkRunnable中:
@Override
public void run() {
//使用Processor去执行任务
mWorkManagerImpl.getProcessor().startWork(mWorkSpecId, mRuntimeExtras);
}
这里使用Processor去执行任务,调用了Processor.startWork():
public boolean startWork(
@NonNull String id,
@Nullable WorkerParameters.RuntimeExtras runtimeExtras) {
WorkerWrapper workWrapper;
synchronized (mLock) {
...
//创建了一个WorkerWrapper,WorkerWrapper是Runnable的包装类
workWrapper =
new WorkerWrapper.Builder(
mAppContext,
mConfiguration,
mWorkTaskExecutor,
this,
mWorkDatabase,
id)
.withSchedulers(mSchedulers)
.withRuntimeExtras(runtimeExtras)
.build();
ListenableFuture future = workWrapper.getFuture();
future.addListener(
new FutureListener(this, id, future),
mWorkTaskExecutor.getMainThreadExecutor());
mEnqueuedWorkMap.put(id, workWrapper);
}
//WorkerWrapper交给WorkTaskExecutor去处理
mWorkTaskExecutor.getBackgroundExecutor().execute(workWrapper);
Logger.get().debug(TAG, String.format("%s: processing %s", getClass().getSimpleName(), id));
return true;
}
进入WorkerWrapper的run方法:
public void run() {
mTags = mWorkTagDao.getTagsForWorkSpecId(mWorkSpecId);
mWorkDescription = createWorkDescription(mTags);
runWorker();
}
接着调用了WorkerWrapper的runWorker()方法:
private void runWorker() {
...
if (trySetRunning()) {
if (tryCheckForInterruptionAndResolve()) {
return;
}
final SettableFuture future = SettableFuture.create();
final WorkForegroundRunnable foregroundRunnable =
new WorkForegroundRunnable(
mAppContext,
mWorkSpec,
mWorker,
params.getForegroundUpdater(),
mWorkTaskExecutor
);
mWorkTaskExecutor.getMainThreadExecutor().execute(foregroundRunnable);
final ListenableFuture runExpedited = foregroundRunnable.getFuture();
runExpedited.addListener(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
runExpedited.get();
Logger.get().debug(TAG,
String.format("Starting work for %s", mWorkSpec.workerClassName));
//这里是开始任务的核心方法
mInnerFuture = mWorker.startWork();
future.setFuture(mInnerFuture);
} catch (Throwable e) {
future.setException(e);
}
}
}, mWorkTaskExecutor.getMainThreadExecutor());
}
...
}
调用mWorker.startWork()来到了ListenableFuture的startWork():
@MainThread
public abstract @NonNull ListenableFuture startWork();
具体实现在Worker类中:
public abstract class Worker extends ListenableWorker {
SettableFuture mFuture;
@Keep
@SuppressLint("BanKeepAnnotation")
public Worker(@NonNull Context context, @NonNull WorkerParameters workerParams) {
super(context, workerParams);
}
@WorkerThread
public abstract @NonNull Result doWork();
@Override
public final @NonNull ListenableFuture startWork() {
mFuture = SettableFuture.create();
getBackgroundExecutor().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Result result = doWork();
mFuture.set(result);
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
mFuture.setException(throwable);
}
}
});
return mFuture;
}
}
而我们自定义的SimpleWorker等类,继承的就是这个Worker类,这样就完成了无约束条件任务的执行。
class SimpleWorker(context: Context, workParams: WorkerParameters) :
Worker(context, workParams) {
companion object {
const val TAG = "---SimpleWorker"
}
override fun doWork(): Result {
Log.d(TAG, "doWork: work start...")
try {
Thread.sleep(3000)
} catch (e: IOException) {
e.printStackTrace()
return Result.failure()
} finally {
Log.d(TAG, "doWork: work end...")
}
return Result.success()
}
}
WorkManager无约束条件任务执行总结:
- WorkManager执行了enqueue()后,创建WorkContinuationImpl对象执行
enqueue()方法。 - WorkContinuationImpl持有的EnqueueRunnable对象将任务添加到db,
并交给Schedulers去调度。 - Schedulers将任务交给每一个Scheduler去处理,GreedyScheduler会先处
理这个任务。 - GreedyScheduler经过一系列判断后,调用WorkManager的startWork()方
法执行这种一次性,非延迟,无约束的任务。 - WorkManager持有的StartWorkRunnable对象会将任务交给Processor去
处理,执行startWork()方法。 - Processor创建一个WorkerWrapper对象,由它去调用Worker的
startWork()方法。
4.3 WorkManager有约束条件任务的执行
反编译或者直接用AndroidStudio打开APK,点开AndroidManifest.xml文件,看到添加了多个receiver,每个receiver对应一个约束条件,比如网络状态:
<receiver
android:name="androidx.work.impl.background.systemalarm.ConstraintProxy$NetworkStateProxy"
android:enabled="false"
android:exported="false"
android:directBootAware="false">
<intent-filter>
<action
android:name="android.net.conn.CONNECTIVITY_CHANGE" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>点进去,来到了ConstraintProxy,它继承了BroadcastReceiver,所以在网络变化、低电量、低内存、充电的时候能接收到系统广播,然后在onReceive进行处理:
abstract class ConstraintProxy extends BroadcastReceiver {
private static final String TAG = Logger.tagWithPrefix("ConstraintProxy");
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Logger.get().debug(TAG, String.format("onReceive : %s", intent));
//创建并启动服务
Intent constraintChangedIntent = CommandHandler.createConstraintsChangedIntent(context);
context.startService(constraintChangedIntent);
}
/**
* Proxy for Battery Not Low constraint
*/
public static class BatteryNotLowProxy extends ConstraintProxy {
}
/**
* Proxy for Battery Charging constraint
*/
public static class BatteryChargingProxy extends ConstraintProxy {
}
/**
* Proxy for Storage Not Low constraint
*/
public static class StorageNotLowProxy extends ConstraintProxy {
}
/**
* Proxy for Network State constraints
*/
public static class NetworkStateProxy extends ConstraintProxy {
}
/**
* Enables/Disables proxies based on constraints in {@link WorkSpec}s
*
* @param context {@link Context}
* @param workSpecs list of {@link WorkSpec}s to update proxies against
*/
static void updateAll(Context context, List workSpecs) {
boolean batteryNotLowProxyEnabled = false;
boolean batteryChargingProxyEnabled = false;
boolean storageNotLowProxyEnabled = false;
boolean networkStateProxyEnabled = false;
for (WorkSpec workSpec : workSpecs) {
Constraints constraints = workSpec.constraints;
batteryNotLowProxyEnabled |= constraints.requiresBatteryNotLow();
batteryChargingProxyEnabled |= constraints.requiresCharging();
storageNotLowProxyEnabled |= constraints.requiresStorageNotLow();
networkStateProxyEnabled |=
constraints.getRequiredNetworkType() != NOT_REQUIRED;
if (batteryNotLowProxyEnabled && batteryChargingProxyEnabled
&& storageNotLowProxyEnabled && networkStateProxyEnabled) {
break;
}
}
Intent updateProxyIntent =
ConstraintProxyUpdateReceiver.newConstraintProxyUpdateIntent(
context,
batteryNotLowProxyEnabled,
batteryChargingProxyEnabled,
storageNotLowProxyEnabled,
networkStateProxyEnabled);
// ConstraintProxies are being updated via a separate broadcast receiver.
// For more information on why we do this look at b/73549299
context.sendBroadcast(updateProxyIntent);
}
}
点击进入CommandHandler.createConstraintsChangedIntent()方法,这里启动了一个SystemAlarmService服务:
static Intent createConstraintsChangedIntent(@NonNull Context context) {
Intent intent = new Intent(context, SystemAlarmService.class);
intent.setAction(ACTION_CONSTRAINTS_CHANGED);
return intent;
}
再进入SystemAlarmService,启动服务后,在onStartCommand中调用SystemAlarmDispatcher.add():
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
if (mIsShutdown) {
Logger.get().info(TAG,
"Re-initializing SystemAlarmDispatcher after a request to shut-down.");
// Destroy the old dispatcher to complete it's lifecycle.
mDispatcher.onDestroy();
// Create a new dispatcher to setup a new lifecycle.
initializeDispatcher();
// Set mIsShutdown to false, to correctly accept new commands.
mIsShutdown = false;
}
if (intent != null) {
//调用SystemAlarmDispatcher.add()
mDispatcher.add(intent, startId);
}
// If the service were to crash, we want all unacknowledged Intents to get redelivered.
return Service.START_REDELIVER_INTENT;
}
然后在SystemAlarmDispatcher的add方法中调用了processCommand():
@MainThread
public boolean add(@NonNull final Intent intent, final int startId) {
...
intent.putExtra(KEY_START_ID, startId);
synchronized (mIntents) {
boolean hasCommands = !mIntents.isEmpty();
mIntents.add(intent);
if (!hasCommands) {
//执行命令
processCommand();
}
}
return true;
}
在SystemAlarmDispatcher.processCommand()中,调用了CommandHandler.onHandleIntent()去处理Intent:
private void processCommand() {
assertMainThread();
PowerManager.WakeLock processCommandLock =
WakeLocks.newWakeLock(mContext, PROCESS_COMMAND_TAG);
try {
processCommandLock.acquire();
// Process commands on the background thread.
mWorkManager.getWorkTaskExecutor().executeOnBackgroundThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (mIntents) {
mCurrentIntent = mIntents.get(0);
}
if (mCurrentIntent != null) {
final String action = mCurrentIntent.getAction();
final int startId = mCurrentIntent.getIntExtra(KEY_START_ID,
DEFAULT_START_ID);
...
final PowerManager.WakeLock wakeLock = WakeLocks.newWakeLock(
mContext,
String.format("%s (%s)", action, startId));
try {
...
wakeLock.acquire();
//这里是核心方法,去处理Intent
mCommandHandler.onHandleIntent(mCurrentIntent, startId,
SystemAlarmDispatcher.this);
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
...
} finally {
...
}
}
}
});
} finally {
processCommandLock.release();
}
}
CommandHandler.onHandleIntent()会对约束条件的改变作出处理:
@WorkerThread
void onHandleIntent(
@NonNull Intent intent,
int startId,
@NonNull SystemAlarmDispatcher dispatcher) {
String action = intent.getAction();
if (ACTION_CONSTRAINTS_CHANGED.equals(action)) {
//带约束条件改变会走这里
handleConstraintsChanged(intent, startId, dispatcher);
} else if (ACTION_RESCHEDULE.equals(action)) {
handleReschedule(intent, startId, dispatcher);
} else {
Bundle extras = intent.getExtras();
if (!hasKeys(extras, KEY_WORKSPEC_ID)) {
Logger.get().error(TAG,
String.format("Invalid request for %s, requires %s.",
action,
KEY_WORKSPEC_ID));
} else {
if (ACTION_SCHEDULE_WORK.equals(action)) {
handleScheduleWorkIntent(intent, startId, dispatcher);
} else if (ACTION_DELAY_MET.equals(action)) {
handleDelayMet(intent, startId, dispatcher);
} else if (ACTION_STOP_WORK.equals(action)) {
handleStopWork(intent, dispatcher);
} else if (ACTION_EXECUTION_COMPLETED.equals(action)) {
handleExecutionCompleted(intent, startId);
} else {
Logger.get().warning(TAG, String.format("Ignoring intent %s", intent));
}
}
}
}
CommandHandler.handleConstraintsChanged()方法中实例化了一个ConstraintsCommandHandler,调用了ConstraintsCommandHandler.handleConstraintsChanged():
private void handleConstraintsChanged(
@NonNull Intent intent, int startId,
@NonNull SystemAlarmDispatcher dispatcher) {
Logger.get().debug(TAG, String.format("Handling constraints changed %s", intent));
// Constraints changed command handler is synchronous. No cleanup
// is necessary.
ConstraintsCommandHandler changedCommandHandler =
new ConstraintsCommandHandler(mContext, startId, dispatcher);
changedCommandHandler.handleConstraintsChanged();
}
在handleConstraintsChanged()中,创建了一个DelayMetIntent交给AddRunnable,然后调用SystemAlarmDispatcher发送出去:
@WorkerThread
void handleConstraintsChanged() {
...
for (WorkSpec workSpec : eligibleWorkSpecs) {
String workSpecId = workSpec.id;
//创建了一个DelayMetIntent,交给AddRunnable,然后SystemAlarmDispatcher发送出去
Intent intent = CommandHandler.createDelayMetIntent(mContext, workSpecId);
Logger.get().debug(TAG, String.format(
"Creating a delay_met command for workSpec with id (%s)", workSpecId));
mDispatcher.postOnMainThread(
new SystemAlarmDispatcher.AddRunnable(mDispatcher, intent, mStartId));
}
...
}
然后AddRunnable的run方法中,又调用了SystemAlarmDispatcher.add():
static class AddRunnable implements Runnable {
private final SystemAlarmDispatcher mDispatcher;
private final Intent mIntent;
private final int mStartId;
AddRunnable(@NonNull SystemAlarmDispatcher dispatcher,
@NonNull Intent intent,
int startId) {
mDispatcher = dispatcher;
mIntent = intent;
mStartId = startId;
}
@Override
public void run() {
mDispatcher.add(mIntent, mStartId);
}
}
SystemAlarmDispatcher.add()中执行processCommand(),然后又到了CommandHandler.onHandleIntent(),而由于这次的Intent是DelayMetIntent,所以这次走的是handleDelayMet:
@WorkerThread
void onHandleIntent(
@NonNull Intent intent,
int startId,
@NonNull SystemAlarmDispatcher dispatcher) {
String action = intent.getAction();
if (ACTION_CONSTRAINTS_CHANGED.equals(action)) {
handleConstraintsChanged(intent, startId, dispatcher);
} else if (ACTION_RESCHEDULE.equals(action)) {
handleReschedule(intent, startId, dispatcher);
} else {
Bundle extras = intent.getExtras();
if (!hasKeys(extras, KEY_WORKSPEC_ID)) {
Logger.get().error(TAG,
String.format("Invalid request for %s, requires %s.",
action,
KEY_WORKSPEC_ID));
} else {
if (ACTION_SCHEDULE_WORK.equals(action)) {
handleScheduleWorkIntent(intent, startId, dispatcher);
} else if (ACTION_DELAY_MET.equals(action)) {
//这一次,会走到这里
handleDelayMet(intent, startId, dispatcher);
} else if (ACTION_STOP_WORK.equals(action)) {
handleStopWork(intent, dispatcher);
} else if (ACTION_EXECUTION_COMPLETED.equals(action)) {
handleExecutionCompleted(intent, startId);
} else {
Logger.get().warning(TAG, String.format("Ignoring intent %s", intent));
}
}
}
}
在CommandHandler.handleDelayMet()中,实例化DelayMetCommandHandler:
private void handleDelayMet(
@NonNull Intent intent,
int startId,
@NonNull SystemAlarmDispatcher dispatcher) {
Bundle extras = intent.getExtras();
synchronized (mLock) {
String workSpecId = extras.getString(KEY_WORKSPEC_ID);
Logger.get().debug(TAG, String.format("Handing delay met for %s", workSpecId));
// Check to see if we are already handling an ACTION_DELAY_MET for the WorkSpec.
// If we are, then there is nothing for us to do.
if (!mPendingDelayMet.containsKey(workSpecId)) {
DelayMetCommandHandler delayMetCommandHandler =
new DelayMetCommandHandler(mContext, startId, workSpecId, dispatcher);
mPendingDelayMet.put(workSpecId, delayMetCommandHandler);
delayMetCommandHandler.handleProcessWork();
} else {
Logger.get().debug(TAG,
String.format("WorkSpec %s is already being handled for ACTION_DELAY_MET",
workSpecId));
}
}
}
在DelayMetCommandHandler中,会执行onAllConstraintsMet方法,onAllConstraintsMet中会从SystemAlarmDispatcher中获取Processor去开始执行任务。后续逻辑就和4.2中StartWorkRunnable中的逻辑一样了。
@Override
public void onAllConstraintsMet(@NonNull List workSpecIds) {
...
synchronized (mLock) {
if (mCurrentState == STATE_INITIAL) {
mCurrentState = STATE_START_REQUESTED;
//通过SystemAlarmDispatcher获取Processor,调用startWork
boolean isEnqueued = mDispatcher.getProcessor().startWork(mWorkSpecId);
...
} else {
Logger.get().debug(TAG, String.format("Already started work for %s", mWorkSpecId));
}
}
}
1、本站所有资源均从互联网上收集整理而来,仅供学习交流之用,因此不包含技术服务请大家谅解!
2、本站不提供任何实质性的付费和支付资源,所有需要积分下载的资源均为网站运营赞助费用或者线下劳务费用!
3、本站所有资源仅用于学习及研究使用,您必须在下载后的24小时内删除所下载资源,切勿用于商业用途,否则由此引发的法律纠纷及连带责任本站和发布者概不承担!
4、本站站内提供的所有可下载资源,本站保证未做任何负面改动(不包含修复bug和完善功能等正面优化或二次开发),但本站不保证资源的准确性、安全性和完整性,用户下载后自行斟酌,我们以交流学习为目的,并不是所有的源码都100%无错或无bug!如有链接无法下载、失效或广告,请联系客服处理!
5、本站资源除标明原创外均来自网络整理,版权归原作者或本站特约原创作者所有,如侵犯到您的合法权益,请立即告知本站,本站将及时予与删除并致以最深的歉意!
6、如果您也有好的资源或教程,您可以投稿发布,成功分享后有站币奖励和额外收入!
7、如果您喜欢该资源,请支持官方正版资源,以得到更好的正版服务!
8、请您认真阅读上述内容,注册本站用户或下载本站资源即您同意上述内容!
原文链接:https://www.dandroid.cn/archives/19430,转载请注明出处。


评论0