本篇介绍
AAudio 是Android O版本引入的C API,专门用于高性能音频场景,本篇介绍下AAudio的内容和框架。
AAudio 功能介绍
共享模式
音频流具有共享模式:
AAUDIO_SHARING_MODE_EXCLUSIVE(独占模式):表示该流独占一个音频设备。如果该音频设备已经在使用中,那么该流可能无法对其进行独占访问。独占流得延时较短,但连接断开的可能性也较大,如果不再需要独占流,应尽快予以关闭,以便其他应用访问该设备。独占流可以最大限度缩短延迟时间。
AAUDIO_SHARING_MODE_SHARED:允许AAudio混合音频,也就是可能和其他流公用同一个设备,AAudio会将分配给同一设备的所有共享流混合。
可以在创建流的时候指定共享模式:
/**
* Request a mode for sharing the device.
*
* The default, if you do not call this function, is {@link #AAUDIO_SHARING_MODE_SHARED}.
*
* The requested sharing mode may not be available.
* The application can query for the actual mode after the stream is opened.
*
* Available since API level 26.
*
* @param builder reference provided by AAudio_createStreamBuilder()
* @param sharingMode {@link #AAUDIO_SHARING_MODE_SHARED} or {@link #AAUDIO_SHARING_MODE_EXCLUSIVE}
*/
AAUDIO_API void AAudioStreamBuilder_setSharingMode(AAudioStreamBuilder* builder,
aaudio_sharing_mode_t sharingMode) __INTRODUCED_IN(26);
性能优化
这儿需要提到两个概念,underrun和overrun。
可以用生产消费者角度看,underrun就是生产者的速度赶不上消费者的速度了,对
于音频,那么就是在音频播放的时候,应用提供数据的速度赶不上AudioFlinger读取的速度了。overrun就是生产者的速度超过了消费者的消耗速度,对于音频,那么就是在音频采集的时候,应用速度采集速度没有AudioFliner提供采集数据速度快。
在音频播放的时候,如果出现underrun,就会表现为卡顿,杂音等。这儿最为关键的就是调整缓存区,缓存区太小,容易出现underrun,缓存区太大,又会增加延时。因此缓存区大小可以按找underrun来调整,刚开始缓存区比较小,然后慢慢增大,例子如下:
int32_t previousUnderrunCount = 0;
int32_t framesPerBurst = AAudioStream_getFramesPerBurst(stream);
int32_t bufferSize = AAudioStream_getBufferSizeInFrames(stream);
int32_t bufferCapacity = AAudioStream_getBufferCapacityInFrames(stream);
while (go) {
result = writeSomeData();
if (result < 0) break;
// Are we getting underruns?
if (bufferSize < bufferCapacity) {
int32_t underrunCount = AAudioStream_getXRunCount(stream);
if (underrunCount > previousUnderrunCount) {
previousUnderrunCount = underrunCount;
// Try increasing the buffer size by one burst
bufferSize += framesPerBurst;
bufferSize = AAudioStream_setBufferSize(stream, bufferSize);
}
}
}
性能模式
每个 AAudioStream 都具有性能模式,而这对应用行为的影响很大。共有三种模式:
AAUDIO_PERFORMANCE_MODE_NONE 是默认模式。这种模式使用在延迟时间与节能之间取得平衡的基本流。
AAUDIO_PERFORMANCE_MODE_LOW_LATENCY 使用较小的缓冲区和经优化的数据路径,以减少延迟时间。
AAUDIO_PERFORMANCE_MODE_POWER_SAVING 使用较大的内部缓冲区,以及以延迟时间为代价换取节能优势的数据路径。
AAudio 源码解读
AAudio使用构建器模式创建AAudioStream,通过AAudioStreamBuilder设置好参数后,接下来就是执行open获取可用的AAudioStream, 调用的方法是AAudioStreamBuilder_openStream:
AAUDIO_API aaudio_result_t AAudioStreamBuilder_openStream(AAudioStreamBuilder* builder,
AAudioStream** streamPtr)
{
AudioStream *audioStream = nullptr;
aaudio_stream_id_t id = 0;
// Please leave these logs because they are very helpful when debugging.
ALOGI("%s() called ----------------------------------------", __func__);
AudioStreamBuilder *streamBuilder = COMMON_GET_FROM_BUILDER_OR_RETURN(streamPtr);
aaudio_result_t result = streamBuilder->build(&audioStream); // 构建audiostream
if (result == AAUDIO_OK) {
audioStream->registerPlayerBase(); // 注册audiostream, 主要是针对播放,这样就可以被系统音量统一控制。
*streamPtr = (AAudioStream*) audioStream;
id = audioStream->getId();
} else {
*streamPtr = nullptr;
}
ALOGI("%s() returns %d = %s for s#%u ----------------",
__func__, result, AAudio_convertResultToText(result), id);
return result;
}
这儿主要是2件事,一个是负责构建AudioStream,一个是负责注册,先看下构建过程。
// Try to open using MMAP path if that is allowed.
// Fall back to Legacy path if MMAP not available.
// Exact behavior is controlled by MMapPolicy.
aaudio_result_t AudioStreamBuilder::build(AudioStream** streamPtr) {
...
// The API setting is the highest priority.
aaudio_policy_t mmapPolicy = AudioGlobal_getMMapPolicy(); //是否走mmap
// If not specified then get from a system property.
if (mmapPolicy == AAUDIO_UNSPECIFIED) {
mmapPolicy = AAudioProperty_getMMapPolicy();
}
// If still not specified then use the default.
if (mmapPolicy == AAUDIO_UNSPECIFIED) {
mmapPolicy = AAUDIO_MMAP_POLICY_DEFAULT;
}
int32_t mapExclusivePolicy = AAudioProperty_getMMapExclusivePolicy();
if (mapExclusivePolicy == AAUDIO_UNSPECIFIED) {
mapExclusivePolicy = AAUDIO_MMAP_EXCLUSIVE_POLICY_DEFAULT;
}
aaudio_sharing_mode_t sharingMode = getSharingMode();
if ((sharingMode == AAUDIO_SHARING_MODE_EXCLUSIVE)
&& (mapExclusivePolicy == AAUDIO_POLICY_NEVER)) {
ALOGD("%s() EXCLUSIVE sharing mode not supported. Use SHARED.", __func__);
sharingMode = AAUDIO_SHARING_MODE_SHARED;
setSharingMode(sharingMode);
}
bool allowMMap = mmapPolicy != AAUDIO_POLICY_NEVER;
bool allowLegacy = mmapPolicy != AAUDIO_POLICY_ALWAYS;
// TODO Support other performance settings in MMAP mode.
// Disable MMAP if low latency not requested.
// 非低延时不支持mmap
if (getPerformanceMode() != AAUDIO_PERFORMANCE_MODE_LOW_LATENCY) {
ALOGD("%s() MMAP not used because AAUDIO_PERFORMANCE_MODE_LOW_LATENCY not requested.",
__func__);
allowMMap = false;
}
// SessionID and Effects are only supported in Legacy mode.
if (getSessionId() != AAUDIO_SESSION_ID_NONE) {
ALOGD("%s() MMAP not used because sessionId specified.", __func__);
allowMMap = false;
}
if (!allowMMap && !allowLegacy) {
ALOGE("%s() no backend available: neither MMAP nor legacy path are allowed", __func__);
return AAUDIO_ERROR_ILLEGAL_ARGUMENT;
}
setPrivacySensitive(false);
if (mPrivacySensitiveReq == PRIVACY_SENSITIVE_DEFAULT) {
// When not explicitly requested, set privacy sensitive mode according to input preset:
// communication and camcorder captures are considered privacy sensitive by default.
aaudio_input_preset_t preset = getInputPreset();
if (preset == AAUDIO_INPUT_PRESET_CAMCORDER
|| preset == AAUDIO_INPUT_PRESET_VOICE_COMMUNICATION) {
setPrivacySensitive(true); // Camera 和通话场景,设置隐私标记
}
} else if (mPrivacySensitiveReq == PRIVACY_SENSITIVE_ENABLED) {
setPrivacySensitive(true);
}
android::sp audioStream;
result = builder_createStream(getDirection(), sharingMode, allowMMap, audioStream);
if (result == AAUDIO_OK) {
// Open the stream using the parameters from the builder.
result = audioStream->open(*this);
if (result != AAUDIO_OK) {
bool isMMap = audioStream->isMMap();
if (isMMap && allowLegacy) {
ALOGV("%s() MMAP stream did not open so try Legacy path", __func__);
// If MMAP stream failed to open then TRY using a legacy stream.
result = builder_createStream(getDirection(), sharingMode,
false, audioStream);
if (result == AAUDIO_OK) {
result = audioStream->open(*this);
}
}
}
if (result == AAUDIO_OK) {
audioStream->logOpen();
*streamPtr = startUsingStream(audioStream);
} // else audioStream will go out of scope and be deleted
}
return result;
}
这儿主要是使用builder_createStream 创建AAudioSream,一个是执行AAudioStream的Open方法:
先看下前者:
static aaudio_result_t builder_createStream(aaudio_direction_t direction,
aaudio_sharing_mode_t sharingMode,
bool tryMMap,
android::sp &stream) {
aaudio_result_t result = AAUDIO_OK;
switch (direction) {
case AAUDIO_DIRECTION_INPUT:
if (tryMMap) {
stream = new AudioStreamInternalCapture(AAudioBinderClient::getInstance(),
false);
} else {
stream = new AudioStreamRecord();
}
break;
case AAUDIO_DIRECTION_OUTPUT:
if (tryMMap) {
stream = new AudioStreamInternalPlay(AAudioBinderClient::getInstance(),
false);
} else {
stream = new AudioStreamTrack();
}
break;
default:
ALOGE("%s() bad direction = %d", __func__, direction);
result = AAUDIO_ERROR_ILLEGAL_ARGUMENT;
}
return result;
}
这儿先看下MMap和传统机制的结构:
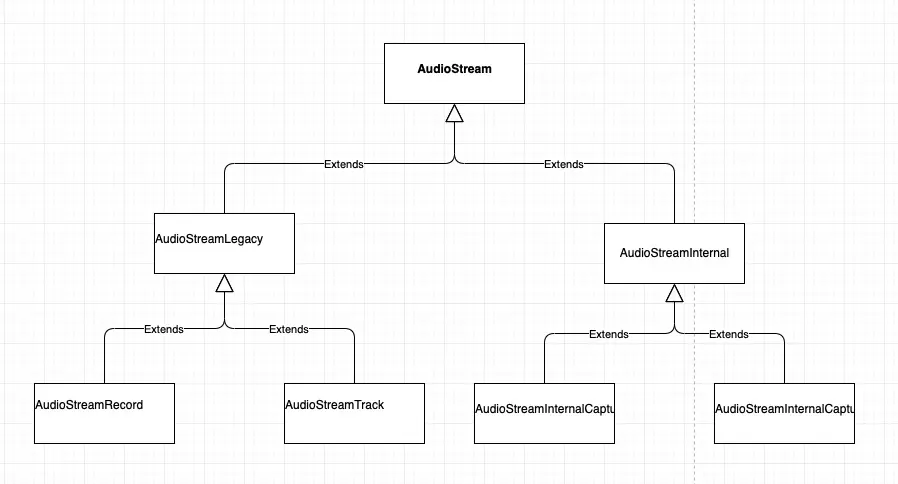
如果是使用非Mmap,并且是采集,那么走的就是AudioStreamRecord,AudioStreamRecord实际上走的就是Java AudioRecord Native通道,AudioStreamRecord内部会创建AudioRecord(C++)对象,其余步骤就和Java的流程一样。
而AAudioStream的open 方法就是创建AudioRecord对象,并且注册设置参数,这时候就会在AudioFlinger中也创建一个对应的AudioRecord对象,并分配对应的缓存。
这儿看下MMap流程,构造方法就是一些赋值,看下open方法:
aaudio_result_t AudioStreamInternal::open(const AudioStreamBuilder &builder) {
aaudio_result_t result = AAUDIO_OK;
int32_t framesPerBurst;
int32_t framesPerHardwareBurst;
AAudioStreamRequest request;
AAudioStreamConfiguration configurationOutput;
if (getState() != AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_UNINITIALIZED) {
ALOGE("%s - already open! state = %d", __func__, getState());
return AAUDIO_ERROR_INVALID_STATE;
}
// Copy requested parameters to the stream.
result = AudioStream::open(builder);
if (result < 0) {
return result;
}
const int32_t burstMinMicros = AAudioProperty_getHardwareBurstMinMicros();
int32_t burstMicros = 0;
// We have to do volume scaling. So we prefer FLOAT format.
if (getFormat() == AUDIO_FORMAT_DEFAULT) {
setFormat(AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_FLOAT);
}
// Request FLOAT for the shared mixer.
request.getConfiguration().setFormat(AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_FLOAT);
// Build the request to send to the server.
request.setUserId(getuid());
request.setProcessId(getpid());
request.setSharingModeMatchRequired(isSharingModeMatchRequired());
request.setInService(isInService());
request.getConfiguration().setDeviceId(getDeviceId());
request.getConfiguration().setSampleRate(getSampleRate());
request.getConfiguration().setSamplesPerFrame(getSamplesPerFrame());
request.getConfiguration().setDirection(getDirection());
request.getConfiguration().setSharingMode(getSharingMode());
request.getConfiguration().setUsage(getUsage());
request.getConfiguration().setContentType(getContentType());
request.getConfiguration().setInputPreset(getInputPreset());
request.getConfiguration().setPrivacySensitive(isPrivacySensitive());
request.getConfiguration().setBufferCapacity(builder.getBufferCapacity());
mDeviceChannelCount = getSamplesPerFrame(); // Assume it will be the same. Update if not.
mServiceStreamHandle = mServiceInterface.openStream(request, configurationOutput); // 1: 打开流
if (mServiceStreamHandle < 0
&& request.getConfiguration().getSamplesPerFrame() == 1 // mono?
&& getDirection() == AAUDIO_DIRECTION_OUTPUT
&& !isInService()) {
// if that failed then try switching from mono to stereo if OUTPUT.
// Only do this in the client. Otherwise we end up with a mono mixer in the service
// that writes to a stereo MMAP stream.
ALOGD("%s() - openStream() returned %d, try switching from MONO to STEREO",
__func__, mServiceStreamHandle);
request.getConfiguration().setSamplesPerFrame(2); // stereo
mServiceStreamHandle = mServiceInterface.openStream(request, configurationOutput);
}
if (mServiceStreamHandle < 0) {
return mServiceStreamHandle;
}
// This must match the key generated in oboeservice/AAudioServiceStreamBase.cpp
// so the client can have permission to log.
mMetricsId = std::string(AMEDIAMETRICS_KEY_PREFIX_AUDIO_STREAM)
+ std::to_string(mServiceStreamHandle);
result = configurationOutput.validate();
if (result != AAUDIO_OK) {
goto error;
}
// Save results of the open.
if (getSamplesPerFrame() == AAUDIO_UNSPECIFIED) {
setSamplesPerFrame(configurationOutput.getSamplesPerFrame());
}
mDeviceChannelCount = configurationOutput.getSamplesPerFrame();
setSampleRate(configurationOutput.getSampleRate());
setDeviceId(configurationOutput.getDeviceId());
setSessionId(configurationOutput.getSessionId());
setSharingMode(configurationOutput.getSharingMode());
setUsage(configurationOutput.getUsage());
setContentType(configurationOutput.getContentType());
setInputPreset(configurationOutput.getInputPreset());
// Save device format so we can do format conversion and volume scaling together.
setDeviceFormat(configurationOutput.getFormat());
result = mServiceInterface.getStreamDescription(mServiceStreamHandle, mEndPointParcelable); // 2. 获取共享内存
if (result != AAUDIO_OK) {
goto error;
}
// Resolve parcelable into a descriptor.
result = mEndPointParcelable.resolve(&mEndpointDescriptor);
if (result != AAUDIO_OK) {
goto error;
}
// Configure endpoint based on descriptor.
mAudioEndpoint = std::make_unique();
result = mAudioEndpoint->configure(&mEndpointDescriptor, getDirection());
if (result != AAUDIO_OK) {
goto error;
}
framesPerHardwareBurst = mEndpointDescriptor.dataQueueDescriptor.framesPerBurst;
// Scale up the burst size to meet the minimum equivalent in microseconds.
// This is to avoid waking the CPU too often when the HW burst is very small
// or at high sample rates.
framesPerBurst = framesPerHardwareBurst;
do {
if (burstMicros > 0) { // skip first loop
framesPerBurst *= 2;
}
burstMicros = framesPerBurst * static_cast(1000000) / getSampleRate();
} while (burstMicros < burstMinMicros);
ALOGD("%s() original HW burst = %d, minMicros = %d => SW burst = %dn",
__func__, framesPerHardwareBurst, burstMinMicros, framesPerBurst);
// Validate final burst size.
if (framesPerBurst < MIN_FRAMES_PER_BURST || framesPerBurst > MAX_FRAMES_PER_BURST) {
ALOGE("%s - framesPerBurst out of range = %d", __func__, framesPerBurst);
result = AAUDIO_ERROR_OUT_OF_RANGE;
goto error;
}
mFramesPerBurst = framesPerBurst; // only save good value
mBufferCapacityInFrames = mEndpointDescriptor.dataQueueDescriptor.capacityInFrames;
if (mBufferCapacityInFrames < mFramesPerBurst
|| mBufferCapacityInFrames > MAX_BUFFER_CAPACITY_IN_FRAMES) {
ALOGE("%s - bufferCapacity out of range = %d", __func__, mBufferCapacityInFrames);
result = AAUDIO_ERROR_OUT_OF_RANGE;
goto error;
}
mClockModel.setSampleRate(getSampleRate());
mClockModel.setFramesPerBurst(framesPerHardwareBurst);
if (isDataCallbackSet()) {
mCallbackFrames = builder.getFramesPerDataCallback();
if (mCallbackFrames > getBufferCapacity() / 2) {
ALOGW("%s - framesPerCallback too big = %d, capacity = %d",
__func__, mCallbackFrames, getBufferCapacity());
result = AAUDIO_ERROR_OUT_OF_RANGE;
goto error;
} else if (mCallbackFrames < 0) {
ALOGW("%s - framesPerCallback negative", __func__);
result = AAUDIO_ERROR_OUT_OF_RANGE;
goto error;
}
if (mCallbackFrames == AAUDIO_UNSPECIFIED) {
mCallbackFrames = mFramesPerBurst;
}
const int32_t callbackBufferSize = mCallbackFrames * getBytesPerFrame();
mCallbackBuffer = std::make_unique(callbackBufferSize);
}
// For debugging and analyzing the distribution of MMAP timestamps.
// For OUTPUT, use a NEGATIVE offset to move the CPU writes further BEFORE the HW reads.
// For INPUT, use a POSITIVE offset to move the CPU reads further AFTER the HW writes.
// You can use this offset to reduce glitching.
// You can also use this offset to force glitching. By iterating over multiple
// values you can reveal the distribution of the hardware timing jitter.
if (mAudioEndpoint->isFreeRunning()) { // MMAP?
int32_t offsetMicros = (getDirection() == AAUDIO_DIRECTION_OUTPUT)
? AAudioProperty_getOutputMMapOffsetMicros()
: AAudioProperty_getInputMMapOffsetMicros();
// This log is used to debug some tricky glitch issues. Please leave.
ALOGD_IF(offsetMicros, "%s() - %s mmap offset = %d micros",
__func__,
(getDirection() == AAUDIO_DIRECTION_OUTPUT) ? "output" : "input",
offsetMicros);
mTimeOffsetNanos = offsetMicros * AAUDIO_NANOS_PER_MICROSECOND;
}
setBufferSize(mBufferCapacityInFrames / 2); // Default buffer size to match Q
setState(AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_OPEN);
return result;
error:
releaseCloseFinal();
return result;
}
先看下怎样打开流:
···
aaudio_handle_t AAudioBinderClient::openStream(const AAudioStreamRequest &request,
AAudioStreamConfiguration &configurationOutput)
{
aaudio_handle_t stream;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
const sp
if (service.get() == nullptr)
return AAUDIO_ERROR_NO_SERVICE;
stream = service->openStream(request, configurationOutput);
if (stream == AAUDIO_ERROR_NO_SERVICE)
{
ALOGE("openStream lost connection to AAudioService.");
dropAAudioService(); // force a reconnect
}
else
{
break;
}
}
return stream;
}
···
这儿就是获取media.aaudio binder服务,然后调用openStream打开流。
media.aaudio就是AAudioService, 代码路径在frameworks/av/services/oboeservice/AAudioService.cpp,看下openStream实现:
···
aaudio_handle_t AAudioService::openStream(const aaudio::AAudioStreamRequest &request,
aaudio::AAudioStreamConfiguration &configurationOutput) {
// A lock in is used to order the opening of endpoints when an
// EXCLUSIVE endpoint is stolen. We want the order to be:
// 1) Thread A opens exclusive MMAP endpoint
// 2) Thread B wants to open an exclusive MMAP endpoint so it steals the one from A
// under this lock.
// 3) Thread B opens a shared MMAP endpoint.
// 4) Thread A can then get the lock and also open a shared stream.
// Without the lock. Thread A might sneak in and reallocate an exclusive stream
// before B can open the shared stream.
std::unique_lock<:recursive_mutex> lock(mOpenLock);
aaudio_result_t result = AAUDIO_OK;
sp serviceStream;
const AAudioStreamConfiguration &configurationInput = request.getConstantConfiguration();
bool sharingModeMatchRequired = request.isSharingModeMatchRequired();
aaudio_sharing_mode_t sharingMode = configurationInput.getSharingMode();
// Enforce limit on client processes.
pid_t pid = request.getProcessId();
if (pid != mAudioClient.clientPid) {
int32_t count = AAudioClientTracker::getInstance().getStreamCount(pid);
if (count >= MAX_STREAMS_PER_PROCESS) { // 单个进程最多创建8个流
ALOGE("openStream(): exceeded max streams per process %d >= %d",
count, MAX_STREAMS_PER_PROCESS);
return AAUDIO_ERROR_UNAVAILABLE;
}
}
if (sharingMode != AAUDIO_SHARING_MODE_EXCLUSIVE && sharingMode != AAUDIO_SHARING_MODE_SHARED) {
ALOGE("openStream(): unrecognized sharing mode = %d", sharingMode);
return AAUDIO_ERROR_ILLEGAL_ARGUMENT;
}
if (sharingMode == AAUDIO_SHARING_MODE_EXCLUSIVE
&& AAudioClientTracker::getInstance().isExclusiveEnabled(request.getProcessId())) {
// only trust audioserver for in service indication
bool inService = false;
if (isCallerInService()) {
inService = request.isInService();
}
serviceStream = new AAudioServiceStreamMMAP(*this, inService);
result = serviceStream->open(request);
if (result != AAUDIO_OK) {
// Clear it so we can possibly fall back to using a shared stream.
ALOGW("openStream(), could not open in EXCLUSIVE mode");
serviceStream.clear();
}
}
// Try SHARED if SHARED requested or if EXCLUSIVE failed.
if (sharingMode == AAUDIO_SHARING_MODE_SHARED) {
serviceStream = new AAudioServiceStreamShared(*this);
result = serviceStream->open(request);
} else if (serviceStream.get() == nullptr && !sharingModeMatchRequired) {
aaudio::AAudioStreamRequest modifiedRequest = request;
// Overwrite the original EXCLUSIVE mode with SHARED.
modifiedRequest.getConfiguration().setSharingMode(AAUDIO_SHARING_MODE_SHARED);
serviceStream = new AAudioServiceStreamShared(*this);
result = serviceStream->open(modifiedRequest);
}
if (result != AAUDIO_OK) {
serviceStream.clear();
return result;
} else {
aaudio_handle_t handle = mStreamTracker.addStreamForHandle(serviceStream.get());
serviceStream->setHandle(handle);
pid_t pid = request.getProcessId();
AAudioClientTracker::getInstance().registerClientStream(pid, serviceStream);
configurationOutput.copyFrom(*serviceStream);
// Log open in MediaMetrics after we have the handle because we need the handle to
// create the metrics ID.
serviceStream->logOpen(handle);
ALOGV("%s(): return handle = 0x%08X", __func__, handle);
return handle;
}
}
···
这儿就是创建一个AAudioServiceStreamMMAP或者AAudioServiceStreamShared,open成功后记录一下,这样在dumpsys的时候就可以看到使用aaudio的应用信息和对应的配置了。
先看下AAudioServiceStreamMMAP和AAudioServiceStreamShared的结构:

这儿继续看下AAudioServiceStreamMMAP的流程:
// Open stream on HAL and pass information about the shared memory buffer back to the client.
aaudio_result_t AAudioServiceStreamMMAP::open(const aaudio::AAudioStreamRequest &request) {
sp keep(this);
if (request.getConstantConfiguration().getSharingMode() != AAUDIO_SHARING_MODE_EXCLUSIVE) {
ALOGE("%s() sharingMode mismatch %d", __func__,
request.getConstantConfiguration().getSharingMode());
return AAUDIO_ERROR_INTERNAL;
}
aaudio_result_t result = AAudioServiceStreamBase::open(request);
if (result != AAUDIO_OK) {
return result;
}
sp endpoint = mServiceEndpointWeak.promote();
if (endpoint == nullptr) {
ALOGE("%s() has no endpoint", __func__);
return AAUDIO_ERROR_INVALID_STATE;
}
result = endpoint->registerStream(keep);
if (result != AAUDIO_OK) {
return result;
}
setState(AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_OPEN);
return AAUDIO_OK;
}
使用了base的open,继续看下:
aaudio_result_t AAudioServiceStreamBase::open(const aaudio::AAudioStreamRequest &request) {
AAudioEndpointManager &mEndpointManager = AAudioEndpointManager::getInstance();
aaudio_result_t result = AAUDIO_OK;
mMmapClient.clientUid = request.getUserId();
mMmapClient.clientPid = request.getProcessId();
mMmapClient.packageName.setTo(String16("")); // TODO What should we do here?
// Limit scope of lock to avoid recursive lock in close().
{
std::lock_guard<:mutex> lock(mUpMessageQueueLock);
if (mUpMessageQueue != nullptr) {
ALOGE("%s() called twice", __func__);
return AAUDIO_ERROR_INVALID_STATE;
}
mUpMessageQueue = new SharedRingBuffer(); // 分配共享内存,这个内存是支持进程间共享的
result = mUpMessageQueue->allocate(sizeof(AAudioServiceMessage),
QUEUE_UP_CAPACITY_COMMANDS);
if (result != AAUDIO_OK) {
goto error;
}
// This is not protected by a lock because the stream cannot be
// referenced until the service returns a handle to the client.
// So only one thread can open a stream.
mServiceEndpoint = mEndpointManager.openEndpoint(mAudioService,
request);
if (mServiceEndpoint == nullptr) {
result = AAUDIO_ERROR_UNAVAILABLE;
goto error;
}
// Save a weak pointer that we will use to access the endpoint.
mServiceEndpointWeak = mServiceEndpoint;
mFramesPerBurst = mServiceEndpoint->getFramesPerBurst();
copyFrom(*mServiceEndpoint);
}
return result;
error:
close();
return result;
}
aaudio_result_t AAudioServiceStreamBase::close() {
std::lock_guard<:mutex> lock(mLock);
return close_l();
}
这儿调用的是openEndpoint:
sp AAudioEndpointManager::openEndpoint(AAudioService &audioService,
const aaudio::AAudioStreamRequest &request) {
if (request.getConstantConfiguration().getSharingMode() == AAUDIO_SHARING_MODE_EXCLUSIVE) {
sp endpointToSteal;
sp foundEndpoint =
openExclusiveEndpoint(audioService, request, endpointToSteal);
if (endpointToSteal.get()) {
endpointToSteal->releaseRegisteredStreams(); // free the MMAP resource
}
return foundEndpoint;
} else {
return openSharedEndpoint(audioService, request);
}
}
继续看下openExclusiveEndpoint:
sp AAudioEndpointManager::openExclusiveEndpoint(
AAudioService &aaudioService,
const aaudio::AAudioStreamRequest &request,
sp &endpointToSteal) {
std::lock_guard<:mutex> lock(mExclusiveLock);
const AAudioStreamConfiguration &configuration = request.getConstantConfiguration();
// Try to find an existing endpoint.
sp endpoint = findExclusiveEndpoint_l(configuration); // 从cache中找对应的endPoint
// If we find an existing one then this one cannot be exclusive.
if (endpoint.get() != nullptr) {
if (kStealingEnabled
&& !endpoint->isForSharing() // not currently SHARED
&& !request.isSharingModeMatchRequired()) { // app did not request a shared stream
ALOGD("%s() endpoint in EXCLUSIVE use. Steal it!", __func__);
mExclusiveStolenCount++;
// Prevent this process from getting another EXCLUSIVE stream.
// This will prevent two clients from colliding after a DISCONNECTION
// when they both try to open an exclusive stream at the same time.
// That can result in a stream getting disconnected between the OPEN
// and START calls. This will help preserve app compatibility.
// An app can avoid having this happen by closing their streams when
// the app is paused.
AAudioClientTracker::getInstance().setExclusiveEnabled(request.getProcessId(), false);
endpointToSteal = endpoint; // return it to caller
}
return nullptr;
} else {
sp endpointMMap = new AAudioServiceEndpointMMAP(aaudioService);
ALOGV("%s(), no match so try to open MMAP %p for dev %d",
__func__, endpointMMap.get(), configuration.getDeviceId());
endpoint = endpointMMap;
aaudio_result_t result = endpoint->open(request);
if (result != AAUDIO_OK) {
endpoint.clear();
} else {
mExclusiveStreams.push_back(endpointMMap);
mExclusiveOpenCount++;
}
}
if (endpoint.get() != nullptr) {
// Increment the reference count under this lock.
endpoint->setOpenCount(endpoint->getOpenCount() + 1);
endpoint->setForSharing(request.isSharingModeMatchRequired());
}
return endpoint;
}
这时候创建了一个AAudioServiceEndpointMMAP,然后调用了open,继续往下看:
aaudio_result_t AAudioServiceEndpointMMAP::open(const aaudio::AAudioStreamRequest &request) {
aaudio_result_t result = AAUDIO_OK;
audio_config_base_t config;
audio_port_handle_t deviceId;
copyFrom(request.getConstantConfiguration());
const audio_attributes_t attributes = getAudioAttributesFrom(this);
mMmapClient.clientUid = request.getUserId();
mMmapClient.clientPid = request.getProcessId();
mMmapClient.packageName.setTo(String16(""));
mRequestedDeviceId = deviceId = getDeviceId();
// Fill in config
audio_format_t audioFormat = getFormat();
if (audioFormat == AUDIO_FORMAT_DEFAULT || audioFormat == AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_FLOAT) {
audioFormat = AUDIO_FORMAT_PCM_16_BIT;
}
config.format = audioFormat;
int32_t aaudioSampleRate = getSampleRate();
if (aaudioSampleRate == AAUDIO_UNSPECIFIED) {
aaudioSampleRate = AAUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_DEFAULT;
}
config.sample_rate = aaudioSampleRate;
int32_t aaudioSamplesPerFrame = getSamplesPerFrame();
const aaudio_direction_t direction = getDirection();
if (direction == AAUDIO_DIRECTION_OUTPUT) {
config.channel_mask = (aaudioSamplesPerFrame == AAUDIO_UNSPECIFIED)
? AUDIO_CHANNEL_OUT_STEREO
: audio_channel_out_mask_from_count(aaudioSamplesPerFrame);
mHardwareTimeOffsetNanos = OUTPUT_ESTIMATED_HARDWARE_OFFSET_NANOS; // frames at DAC later
} else if (direction == AAUDIO_DIRECTION_INPUT) {
config.channel_mask = (aaudioSamplesPerFrame == AAUDIO_UNSPECIFIED)
? AUDIO_CHANNEL_IN_STEREO
: audio_channel_in_mask_from_count(aaudioSamplesPerFrame);
mHardwareTimeOffsetNanos = INPUT_ESTIMATED_HARDWARE_OFFSET_NANOS; // frames at ADC earlier
} else {
ALOGE("%s() invalid direction = %d", __func__, direction);
return AAUDIO_ERROR_ILLEGAL_ARGUMENT;
}
MmapStreamInterface::stream_direction_t streamDirection =
(direction == AAUDIO_DIRECTION_OUTPUT)
? MmapStreamInterface::DIRECTION_OUTPUT
: MmapStreamInterface::DIRECTION_INPUT;
aaudio_session_id_t requestedSessionId = getSessionId();
audio_session_t sessionId = AAudioConvert_aaudioToAndroidSessionId(requestedSessionId);
// Open HAL stream. Set mMmapStream
status_t status = MmapStreamInterface::openMmapStream(streamDirection,
&attributes,
&config,
mMmapClient,
&deviceId,
&sessionId,
this, // callback
mMmapStream,
&mPortHandle);
ALOGD("%s() mMapClient.uid = %d, pid = %d => portHandle = %dn",
__func__, mMmapClient.clientUid, mMmapClient.clientPid, mPortHandle);
if (status != OK) {
// This can happen if the resource is busy or the config does
// not match the hardware.
ALOGD("%s() - openMmapStream() returned status %d", __func__, status);
return AAUDIO_ERROR_UNAVAILABLE;
}
if (deviceId == AAUDIO_UNSPECIFIED) {
ALOGW("%s() - openMmapStream() failed to set deviceId", __func__);
}
setDeviceId(deviceId);
if (sessionId == AUDIO_SESSION_ALLOCATE) {
ALOGW("%s() - openMmapStream() failed to set sessionId", __func__);
}
aaudio_session_id_t actualSessionId =
(requestedSessionId == AAUDIO_SESSION_ID_NONE)
? AAUDIO_SESSION_ID_NONE
: (aaudio_session_id_t) sessionId;
setSessionId(actualSessionId);
ALOGD("%s() deviceId = %d, sessionId = %d", __func__, getDeviceId(), getSessionId());
// Create MMAP/NOIRQ buffer.
int32_t minSizeFrames = getBufferCapacity();
if (minSizeFrames <= 0) { // zero will get rejected
minSizeFrames = AAUDIO_BUFFER_CAPACITY_MIN;
}
status = mMmapStream->createMmapBuffer(minSizeFrames, &mMmapBufferinfo);
bool isBufferShareable = mMmapBufferinfo.flags & AUDIO_MMAP_APPLICATION_SHAREABLE;
if (status != OK) {
ALOGE("%s() - createMmapBuffer() failed with status %d %s",
__func__, status, strerror(-status));
result = AAUDIO_ERROR_UNAVAILABLE;
goto error;
} else {
ALOGD("%s() createMmapBuffer() buffer_size = %d fr, burst_size %d fr"
", Sharable FD: %s",
__func__,
mMmapBufferinfo.buffer_size_frames,
mMmapBufferinfo.burst_size_frames,
isBufferShareable ? "Yes" : "No");
}
setBufferCapacity(mMmapBufferinfo.buffer_size_frames);
if (!isBufferShareable) {
// Exclusive mode can only be used by the service because the FD cannot be shared.
uid_t audioServiceUid = getuid();
if ((mMmapClient.clientUid != audioServiceUid) &&
getSharingMode() == AAUDIO_SHARING_MODE_EXCLUSIVE) {
ALOGW("%s() - exclusive FD cannot be used by client", __func__);
result = AAUDIO_ERROR_UNAVAILABLE;
goto error;
}
}
// Get information about the stream and pass it back to the caller.
setSamplesPerFrame((direction == AAUDIO_DIRECTION_OUTPUT)
? audio_channel_count_from_out_mask(config.channel_mask)
: audio_channel_count_from_in_mask(config.channel_mask));
// AAudio creates a copy of this FD and retains ownership of the copy.
// Assume that AudioFlinger will close the original shared_memory_fd.
mAudioDataFileDescriptor.reset(dup(mMmapBufferinfo.shared_memory_fd));
if (mAudioDataFileDescriptor.get() == -1) {
ALOGE("%s() - could not dup shared_memory_fd", __func__);
result = AAUDIO_ERROR_INTERNAL;
goto error;
}
mFramesPerBurst = mMmapBufferinfo.burst_size_frames;
setFormat(config.format);
setSampleRate(config.sample_rate);
ALOGD("%s() actual rate = %d, channels = %d"
", deviceId = %d, capacity = %dn",
__func__, getSampleRate(), getSamplesPerFrame(), deviceId, getBufferCapacity());
ALOGD("%s() format = 0x%08x, frame size = %d, burst size = %d",
__func__, getFormat(), calculateBytesPerFrame(), mFramesPerBurst);
return result;
error:
close();
return result;
}
这儿会创建流和共享buffer,看下openMmapStream:
//static
__attribute__ ((visibility ("default")))
status_t MmapStreamInterface::openMmapStream(MmapStreamInterface::stream_direction_t direction,
const audio_attributes_t *attr,
audio_config_base_t *config,
const AudioClient& client,
audio_port_handle_t *deviceId,
audio_session_t *sessionId,
const sp& callback,
sp& interface,
audio_port_handle_t *handle)
{
sp af;
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(gLock);
af = gAudioFlinger.promote();
}
status_t ret = NO_INIT;
if (af != 0) {
ret = af->openMmapStream(
direction, attr, config, client, deviceId,
sessionId, callback, interface, handle);
}
return ret;
}
这儿终于到了AudioFlinger,再到AudioFlinger看下:
status_t AudioFlinger::openMmapStream(MmapStreamInterface::stream_direction_t direction,
const audio_attributes_t *attr,
audio_config_base_t *config,
const AudioClient& client,
audio_port_handle_t *deviceId,
audio_session_t *sessionId,
const sp& callback,
sp& interface,
audio_port_handle_t *handle)
{
status_t ret = initCheck();
if (ret != NO_ERROR) {
return ret;
}
audio_session_t actualSessionId = *sessionId;
if (actualSessionId == AUDIO_SESSION_ALLOCATE) {
actualSessionId = (audio_session_t) newAudioUniqueId(AUDIO_UNIQUE_ID_USE_SESSION);
}
audio_stream_type_t streamType = AUDIO_STREAM_DEFAULT;
audio_io_handle_t io = AUDIO_IO_HANDLE_NONE;
audio_port_handle_t portId = AUDIO_PORT_HANDLE_NONE;
audio_attributes_t localAttr = *attr;
if (direction == MmapStreamInterface::DIRECTION_OUTPUT) {
audio_config_t fullConfig = AUDIO_CONFIG_INITIALIZER;
fullConfig.sample_rate = config->sample_rate;
fullConfig.channel_mask = config->channel_mask;
fullConfig.format = config->format;
std::vector secondaryOutputs;
ret = AudioSystem::getOutputForAttr(&localAttr, &io,
actualSessionId,
&streamType, client.clientPid, client.clientUid,
&fullConfig,
(audio_output_flags_t)(AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_MMAP_NOIRQ |
AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_DIRECT),
deviceId, &portId, &secondaryOutputs);
ALOGW_IF(!secondaryOutputs.empty(),
"%s does not support secondary outputs, ignoring them", __func__);
} else {
ret = AudioSystem::getInputForAttr(&localAttr, &io,
RECORD_RIID_INVALID,
actualSessionId,
client.clientPid,
client.clientUid,
client.packageName,
config,
AUDIO_INPUT_FLAG_MMAP_NOIRQ, deviceId, &portId);
}
if (ret != NO_ERROR) {
return ret;
}
// at this stage, a MmapThread was created when openOutput() or openInput() was called by
// audio policy manager and we can retrieve it
sp thread = mMmapThreads.valueFor(io);
if (thread != 0) {
interface = new MmapThreadHandle(thread);
thread->configure(&localAttr, streamType, actualSessionId, callback, *deviceId, portId);
*handle = portId;
*sessionId = actualSessionId;
config->sample_rate = thread->sampleRate();
config->channel_mask = thread->channelMask();
config->format = thread->format();
} else {
if (direction == MmapStreamInterface::DIRECTION_OUTPUT) {
AudioSystem::releaseOutput(portId);
} else {
AudioSystem::releaseInput(portId);
}
ret = NO_INIT;
}
ALOGV("%s done status %d portId %d", __FUNCTION__, ret, portId);
return ret;
}
这时候就可以通过MmapThread和Hal层读写数据了。
这儿还返回了一个interface,就是MmapThreadHandle对象,用来共享内存的。
接下来调用interface的createMmapBuffer来创建共享内存:
status_t AudioFlinger::MmapThreadHandle::createMmapBuffer(int32_t minSizeFrames,
struct audio_mmap_buffer_info *info)
{
return mThread->createMmapBuffer(minSizeFrames, info);
}
status_t AudioFlinger::MmapThread::createMmapBuffer(int32_t minSizeFrames,
struct audio_mmap_buffer_info *info)
{
if (mHalStream == 0) {
return NO_INIT;
}
mStandby = true;
acquireWakeLock();
return mHalStream->createMmapBuffer(minSizeFrames, info);
}
这时候就走到了Hal层创建共享内存了。
这时候就完成流的创建了。
接下来继续看下如何启动,入口是AAudioStream_requestStart:
AAUDIO_API aaudio_result_t AAudioStream_requestStart(AAudioStream* stream)
{
AudioStream *audioStream = convertAAudioStreamToAudioStream(stream);
aaudio_stream_id_t id = audioStream->getId();
ALOGD("%s(s#%u) called --------------", __func__, id);
aaudio_result_t result = audioStream->systemStart();
ALOGD("%s(s#%u) returned %d ---------", __func__, id, result);
return result;
}
这时候就是直接调用AudioStream的systemStart 方法:
aaudio_result_t AudioStream::systemStart() {
std::lock_guard<:mutex> lock(mStreamLock);
if (collidesWithCallback()) {
ALOGE("%s cannot be called from a callback!", __func__);
return AAUDIO_ERROR_INVALID_STATE;
}
switch (getState()) {
// Is this a good time to start?
case AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_OPEN:
case AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_PAUSING:
case AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_PAUSED:
case AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_STOPPING:
case AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_STOPPED:
case AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_FLUSHING:
case AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_FLUSHED:
break; // Proceed with starting.
// Already started?
case AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_STARTING:
case AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_STARTED:
ALOGW("%s() stream was already started, state = %s", __func__,
AudioGlobal_convertStreamStateToText(getState()));
return AAUDIO_ERROR_INVALID_STATE;
// Don't start when the stream is dead!
case AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_DISCONNECTED:
case AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_CLOSING:
case AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_CLOSED:
default:
ALOGW("%s() stream is dead, state = %s", __func__,
AudioGlobal_convertStreamStateToText(getState()));
return AAUDIO_ERROR_INVALID_STATE;
}
aaudio_result_t result = requestStart();
if (result == AAUDIO_OK) {
// We only call this for logging in "dumpsys audio". So ignore return code.
(void) mPlayerBase->start();
}
return result;
}
这儿会有一个检查,不可以在回调里面调用Start,检查通过后,接下来调用requestStart,对于legacy,那么实现如下:
aaudio_result_t AudioStreamRecord::requestStart()
{
if (mAudioRecord.get() == nullptr) {
return AAUDIO_ERROR_INVALID_STATE;
}
// Enable callback before starting AudioRecord to avoid shutting
// down because of a race condition.
mCallbackEnabled.store(true);
aaudio_stream_state_t originalState = getState();
// Set before starting the callback so that we are in the correct state
// before updateStateMachine() can be called by the callback.
setState(AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_STARTING);
mFramesWritten.reset32(); // service writes frames
mTimestampPosition.reset32();
status_t err = mAudioRecord->start(); // resets position to zero
if (err != OK) {
mCallbackEnabled.store(false);
setState(originalState);
return AAudioConvert_androidToAAudioResult(err);
}
return AAUDIO_OK;
}
这儿逻辑比较清晰,就是直接调用AudioRecord的start,其余方法也类似。接下来看下Mmap的实现:
aaudio_result_t AudioStreamInternal::requestStart()
{
int64_t startTime;
if (mServiceStreamHandle == AAUDIO_HANDLE_INVALID) {
ALOGD("requestStart() mServiceStreamHandle invalid");
return AAUDIO_ERROR_INVALID_STATE;
}
if (isActive()) {
ALOGD("requestStart() already active");
return AAUDIO_ERROR_INVALID_STATE;
}
aaudio_stream_state_t originalState = getState();
if (originalState == AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_DISCONNECTED) {
ALOGD("requestStart() but DISCONNECTED");
return AAUDIO_ERROR_DISCONNECTED;
}
setState(AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_STARTING);
// Clear any stale timestamps from the previous run.
drainTimestampsFromService();
aaudio_result_t result = mServiceInterface.startStream(mServiceStreamHandle); // 请求启动
if (result == AAUDIO_ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE) {
ALOGD("%s() INVALID_HANDLE, stream was probably stolen", __func__);
// Stealing was added in R. Coerce result to improve backward compatibility.
result = AAUDIO_ERROR_DISCONNECTED;
setState(AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_DISCONNECTED);
}
startTime = AudioClock::getNanoseconds();
mClockModel.start(startTime);
mNeedCatchUp.request(); // Ask data processing code to catch up when first timestamp received.
// Start data callback thread.
if (result == AAUDIO_OK && isDataCallbackSet()) {
// Launch the callback loop thread.
int64_t periodNanos = mCallbackFrames
* AAUDIO_NANOS_PER_SECOND
/ getSampleRate();
mCallbackEnabled.store(true);
result = createThread(periodNanos, aaudio_callback_thread_proc, this); // 如果是异步形式,就创建一个线程
}
if (result != AAUDIO_OK) {
setState(originalState);
}
return result;
}
请求启动比较复杂,先看下异步线程:
// This is not exposed in the API.
// But it is still used internally to implement callbacks for MMAP mode.
aaudio_result_t AudioStream::createThread(int64_t periodNanoseconds,
aaudio_audio_thread_proc_t threadProc,
void* threadArg)
{
if (mHasThread) {
ALOGE("createThread() - mHasThread already true");
return AAUDIO_ERROR_INVALID_STATE;
}
if (threadProc == nullptr) {
return AAUDIO_ERROR_NULL;
}
// Pass input parameters to the background thread.
mThreadProc = threadProc;
mThreadArg = threadArg;
setPeriodNanoseconds(periodNanoseconds);
int err = pthread_create(&mThread, nullptr, AudioStream_internalThreadProc, this);
if (err != 0) {
android::status_t status = -errno;
ALOGE("createThread() - pthread_create() failed, %d", status);
return AAudioConvert_androidToAAudioResult(status);
} else {
// TODO Use AAudioThread or maybe AndroidThread
// Name the thread with an increasing index, "AAudio_#", for debugging.
static std::atomic nextThreadIndex{1};
char name[16]; // max length for a pthread_name
uint32_t index = nextThreadIndex++;
// Wrap the index so that we do not hit the 16 char limit
// and to avoid hard-to-read large numbers.
index = index % 100000; // arbitrary
snprintf(name, sizeof(name), "AAudio_%u", index);
err = pthread_setname_np(mThread, name);
ALOGW_IF((err != 0), "Could not set name of AAudio thread. err = %d", err);
mHasThread = true;
return AAUDIO_OK;
}
}
这儿没啥逻辑,就是创建了一个线程,看下aaudio_callback_thread_proc是什么:
static void *aaudio_callback_thread_proc(void *context)
{
AudioStreamInternal *stream = (AudioStreamInternal *)context;
//LOGD("oboe_callback_thread, stream = %p", stream);
if (stream != NULL) {
return stream->callbackLoop();
} else {
return NULL;
}
}
这儿就是回调调用方,继续再看看:
// Read data from the stream and pass it to the callback for processing.
void *AudioStreamInternalCapture::callbackLoop() {
aaudio_result_t result = AAUDIO_OK;
aaudio_data_callback_result_t callbackResult = AAUDIO_CALLBACK_RESULT_CONTINUE;
if (!isDataCallbackSet()) return NULL;
// result might be a frame count
while (mCallbackEnabled.load() && isActive() && (result >= 0)) {
// Read audio data from stream.
int64_t timeoutNanos = calculateReasonableTimeout(mCallbackFrames);
// This is a BLOCKING READ!
result = read(mCallbackBuffer.get(), mCallbackFrames, timeoutNanos);
if ((result != mCallbackFrames)) {
ALOGE("callbackLoop: read() returned %d", result);
if (result >= 0) {
// Only read some of the frames requested. Must have timed out.
result = AAUDIO_ERROR_TIMEOUT;
}
maybeCallErrorCallback(result);
break;
}
// Call application using the AAudio callback interface.
callbackResult = maybeCallDataCallback(mCallbackBuffer.get(), mCallbackFrames);
if (callbackResult == AAUDIO_CALLBACK_RESULT_STOP) {
ALOGD("%s(): callback returned AAUDIO_CALLBACK_RESULT_STOP", __func__);
result = systemStopFromCallback();
break;
}
}
ALOGD("callbackLoop() exiting, result = %d, isActive() = %d",
result, (int) isActive());
return NULL;
}
再看下maybeCallDataCallback:
aaudio_data_callback_result_t AudioStream::maybeCallDataCallback(void *audioData,
int32_t numFrames) {
aaudio_data_callback_result_t result = AAUDIO_CALLBACK_RESULT_STOP;
AAudioStream_dataCallback dataCallback = getDataCallbackProc();
if (dataCallback != nullptr) {
// Store thread ID of caller to detect stop() and close() calls from callback.
pid_t expected = CALLBACK_THREAD_NONE;
if (mDataCallbackThread.compare_exchange_strong(expected, gettid())) {
result = (*dataCallback)(
(AAudioStream *) this,
getDataCallbackUserData(),
audioData,
numFrames);
mDataCallbackThread.store(CALLBACK_THREAD_NONE);
} else {
ALOGW("%s() data callback already running!", __func__);
}
}
return result;
}
这儿的dataCallback 就是应用方注册进来的函数指针。
先继续看看startStream,实现到了AAudioService里:
aaudio_result_t AAudioService::startStream(aaudio_handle_t streamHandle) {
sp serviceStream = convertHandleToServiceStream(streamHandle);
if (serviceStream.get() == nullptr) {
ALOGW("%s(), invalid streamHandle = 0x%0x", __func__, streamHandle);
return AAUDIO_ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE;
}
return serviceStream->start();
}
继续跟下start:
aaudio_result_t AAudioServiceStreamBase::start() {
std::lock_guard<:mutex> lock(mLock);
const int64_t beginNs = AudioClock::getNanoseconds();
aaudio_result_t result = AAUDIO_OK;
if (auto state = getState();
state == AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_CLOSED || state == AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_DISCONNECTED) {
ALOGW("%s() already CLOSED, returns INVALID_STATE, handle = %d",
__func__, getHandle());
return AAUDIO_ERROR_INVALID_STATE;
}
mediametrics::Defer defer([&] {
mediametrics::LogItem(mMetricsId)
.set(AMEDIAMETRICS_PROP_EVENT, AMEDIAMETRICS_PROP_EVENT_VALUE_START)
.set(AMEDIAMETRICS_PROP_EXECUTIONTIMENS, (int64_t)(AudioClock::getNanoseconds() - beginNs))
.set(AMEDIAMETRICS_PROP_STATE, AudioGlobal_convertStreamStateToText(getState()))
.set(AMEDIAMETRICS_PROP_STATUS, (int32_t)result)
.record(); });
if (isRunning()) {
return result;
}
setFlowing(false);
setSuspended(false);
// Start with fresh presentation timestamps.
mAtomicStreamTimestamp.clear();
mClientHandle = AUDIO_PORT_HANDLE_NONE;
result = startDevice();
if (result != AAUDIO_OK) goto error;
// This should happen at the end of the start.
sendServiceEvent(AAUDIO_SERVICE_EVENT_STARTED);
setState(AAUDIO_STREAM_STATE_STARTED);
mThreadEnabled.store(true);
result = mTimestampThread.start(this);
if (result != AAUDIO_OK) goto error;
return result;
error:
disconnect_l();
return result;
}
调用了startDevice:
aaudio_result_t AAudioServiceStreamBase::startDevice() {
mClientHandle = AUDIO_PORT_HANDLE_NONE;
sp endpoint = mServiceEndpointWeak.promote();
if (endpoint == nullptr) {
ALOGE("%s() has no endpoint", __func__);
return AAUDIO_ERROR_INVALID_STATE;
}
return endpoint->startStream(this, &mClientHandle);
}
继续跟下:
aaudio_result_t AAudioServiceEndpointMMAP::startStream(sp stream,
audio_port_handle_t *clientHandle __unused) {
// Start the client on behalf of the AAudio service.
// Use the port handle that was provided by openMmapStream().
audio_port_handle_t tempHandle = mPortHandle;
audio_attributes_t attr = {};
if (stream != nullptr) {
attr = getAudioAttributesFrom(stream.get());
}
aaudio_result_t result = startClient(
mMmapClient, stream == nullptr ? nullptr : &attr, &tempHandle);
// When AudioFlinger is passed a valid port handle then it should not change it.
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(tempHandle != mPortHandle,
"%s() port handle not expected to change from %d to %d",
__func__, mPortHandle, tempHandle);
ALOGV("%s() mPortHandle = %d", __func__, mPortHandle);
return result;
}
调用了startClient:
aaudio_result_t AAudioServiceEndpointMMAP::startClient(const android::AudioClient& client,
const audio_attributes_t *attr,
audio_port_handle_t *clientHandle) {
if (mMmapStream == nullptr) return AAUDIO_ERROR_NULL;
status_t status = mMmapStream->start(client, attr, clientHandle);
return AAudioConvert_androidToAAudioResult(status);
}
mMmapStream 就是之前从AuidoFlinger中拿到的共享内存对象MmapThreadHandle,继续看下start:
status_t AudioFlinger::MmapThreadHandle::start(const AudioClient& client,
const audio_attributes_t *attr, audio_port_handle_t *handle)
{
return mThread->start(client, attr, handle);
}
调用的是MmapThread的start:
status_t AudioFlinger::MmapThread::start(const AudioClient& client,
const audio_attributes_t *attr,
audio_port_handle_t *handle)
{
ALOGV("%s clientUid %d mStandby %d mPortId %d *handle %d", __FUNCTION__,
client.clientUid, mStandby, mPortId, *handle);
if (mHalStream == 0) {
return NO_INIT;
}
status_t ret;
if (*handle == mPortId) {
// for the first track, reuse portId and session allocated when the stream was opened
return exitStandby();
}
audio_port_handle_t portId = AUDIO_PORT_HANDLE_NONE;
audio_io_handle_t io = mId;
if (isOutput()) {
audio_config_t config = AUDIO_CONFIG_INITIALIZER;
config.sample_rate = mSampleRate;
config.channel_mask = mChannelMask;
config.format = mFormat;
audio_stream_type_t stream = streamType();
audio_output_flags_t flags =
(audio_output_flags_t)(AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_MMAP_NOIRQ | AUDIO_OUTPUT_FLAG_DIRECT);
audio_port_handle_t deviceId = mDeviceId;
std::vector secondaryOutputs;
ret = AudioSystem::getOutputForAttr(&mAttr, &io,
mSessionId,
&stream,
client.clientPid,
client.clientUid,
&config,
flags,
&deviceId,
&portId,
&secondaryOutputs);
ALOGD_IF(!secondaryOutputs.empty(),
"MmapThread::start does not support secondary outputs, ignoring them");
} else {
audio_config_base_t config;
config.sample_rate = mSampleRate;
config.channel_mask = mChannelMask;
config.format = mFormat;
audio_port_handle_t deviceId = mDeviceId;
ret = AudioSystem::getInputForAttr(&mAttr, &io,
RECORD_RIID_INVALID,
mSessionId,
client.clientPid,
client.clientUid,
client.packageName,
&config,
AUDIO_INPUT_FLAG_MMAP_NOIRQ,
&deviceId,
&portId);
}
// APM should not chose a different input or output stream for the same set of attributes
// and audo configuration
if (ret != NO_ERROR || io != mId) {
ALOGE("%s: error getting output or input from APM (error %d, io %d expected io %d)",
__FUNCTION__, ret, io, mId);
return BAD_VALUE;
}
if (isOutput()) {
ret = AudioSystem::startOutput(portId);
} else {
ret = AudioSystem::startInput(portId);
}
Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock);
// abort if start is rejected by audio policy manager
if (ret != NO_ERROR) {
ALOGE("%s: error start rejected by AudioPolicyManager = %d", __FUNCTION__, ret);
if (!mActiveTracks.isEmpty()) {
mLock.unlock();
if (isOutput()) {
AudioSystem::releaseOutput(portId);
} else {
AudioSystem::releaseInput(portId);
}
mLock.lock();
} else {
mHalStream->stop();
}
return PERMISSION_DENIED;
}
// Given that MmapThread::mAttr is mutable, should a MmapTrack have attributes ?
sp track = new MmapTrack(this, attr == nullptr ? mAttr : *attr, mSampleRate, mFormat,
mChannelMask, mSessionId, isOutput(), client.clientUid,
client.clientPid, IPCThreadState::self()->getCallingPid(),
portId);
if (isOutput()) {
// force volume update when a new track is added
mHalVolFloat = -1.0f;
} else if (!track->isSilenced_l()) {
for (const sp &t : mActiveTracks) {
if (t->isSilenced_l() && t->uid() != client.clientUid)
t->invalidate();
}
}
mActiveTracks.add(track);
sp chain = getEffectChain_l(mSessionId);
if (chain != 0) {
chain->setStrategy(AudioSystem::getStrategyForStream(streamType()));
chain->incTrackCnt();
chain->incActiveTrackCnt();
}
track->logBeginInterval(patchSinksToString(&mPatch)); // log to MediaMetrics
*handle = portId;
broadcast_l();
ALOGV("%s DONE handle %d stream %p", __FUNCTION__, *handle, mHalStream.get());
return NO_ERROR;
}
这儿就将完成了start,其余stop,pause等都类似,不需要再重复。
1、本站所有资源均从互联网上收集整理而来,仅供学习交流之用,因此不包含技术服务请大家谅解!
2、本站不提供任何实质性的付费和支付资源,所有需要积分下载的资源均为网站运营赞助费用或者线下劳务费用!
3、本站所有资源仅用于学习及研究使用,您必须在下载后的24小时内删除所下载资源,切勿用于商业用途,否则由此引发的法律纠纷及连带责任本站和发布者概不承担!
4、本站站内提供的所有可下载资源,本站保证未做任何负面改动(不包含修复bug和完善功能等正面优化或二次开发),但本站不保证资源的准确性、安全性和完整性,用户下载后自行斟酌,我们以交流学习为目的,并不是所有的源码都100%无错或无bug!如有链接无法下载、失效或广告,请联系客服处理!
5、本站资源除标明原创外均来自网络整理,版权归原作者或本站特约原创作者所有,如侵犯到您的合法权益,请立即告知本站,本站将及时予与删除并致以最深的歉意!
6、如果您也有好的资源或教程,您可以投稿发布,成功分享后有站币奖励和额外收入!
7、如果您喜欢该资源,请支持官方正版资源,以得到更好的正版服务!
8、请您认真阅读上述内容,注册本站用户或下载本站资源即您同意上述内容!
原文链接:https://www.dandroid.cn/archives/12444,转载请注明出处。


评论0